In tiny houses, every square inch is maximized for efficiency and functionality. Plumbing is crucial in ensuring your daily needs are met without compromise and the lifeline that keeps everything flowing smoothly. But how does plumbing work in these tiny abodes?
Tiny houses typically utilize compact plumbing systems to conserve space. Systems might connect to the primary sewage or use composting toilets, and for water supply, they either hook up to a municipal source or harvest rainwater. Greywater systems can also be implemented.
This article will delve into all things related to tiny house plumbing. We will explore various systems and their benefits, discuss waste management solutions, and uncover challenges tiny homeowners face along with their ingenious solutions.
Importance of Efficient Plumbing in Tiny Living
Efficient water usage is crucial in tiny houses to ensure every drop counts and minimize waste. Adhering to plumbing regulations becomes even more critical when you have limited space and resources.
One of the key aspects of efficient plumbing in tiny houses is using DIY plumbing solutions. These can help save money and provide customized options for your specific needs. There are various ways to maximize water efficiency, from installing low-flow faucets and showerheads to utilizing greywater systems.
Regular plumbing maintenance is also essential in tiny houses. Checking leaks, inspecting pipes for damage or blockages, and ensuring proper insulation can prevent costly repairs. Investing in a reliable filtration system also ensures you access high-quality water without relying on external sources.
Efficient plumbing plays a significant role in tiny living by optimizing water usage, complying with tiny house regulations, providing DIY solutions, maintaining the system regularly, and incorporating reliable water filtration systems.
Traditional House vs. Tiny House Plumbing
Regarding plumbing, traditional and tiny houses have distinct differences rooted in their underlying philosophies of space and resource utilization.
In a traditional house, the plumbing system is typically larger in scale and designed to accommodate multiple bathrooms and appliances. Tiny house plumbing, on the other hand, is much smaller and simplified due to limited space and resources.
Traditional House Plumbing
With their more abundant space, traditional houses often have elaborate plumbing systems, incorporating multiple bathrooms, larger water heaters, and extensive pipe networks. These systems, while effective, can be resource-intensive and might not prioritize efficiency or conservation.
Traditional house plumbing aims to provide a comfortable living environment while minimizing water waste and promoting sustainability. Homeowners can save resources in a traditional house by implementing efficient and environmentally conscious practices.
Tiny House Plumbing
In contrast, tiny houses prioritize space-saving and often sustainability. Given their limited square footage, the plumbing systems in tiny homes are designed to be compact and efficient. This might mean using smaller, on-demand water heaters, fewer fixtures, and sometimes innovative solutions like composting toilets or greywater recycling systems.
While traditional homes can afford separate systems for potable and non-potable water, tiny homes often consolidate these to maximize space and efficiency. Tiny houses have specific plumbing designs tailored to their limited space to ensure a sufficient water supply. These designs must also adhere to regulations set by local authorities.
Tiny house plumbing regulations vary depending on the jurisdiction, but they typically require specific components such as a water heater, sink, shower, and toilet. The challenge lies in designing a system that maximizes efficiency while minimizing costs.
The core difference lies in the approach: traditional home plumbing focuses on comfort and convenience without space constraints, while tiny home plumbing is all about optimizing space, reducing waste, and minimizing the home’s environmental footprint.
After diving deep into the nuances of traditional house vs. tiny house plumbing, you might also be interested in another intriguing comparison: container home vs tiny home.
Types of Plumbing Systems in Tiny Houses
In discussing the types of plumbing systems in tiny houses, it’s essential to consider both on-grid and off-grid options.
On-grid
Regarding plumbing in on-grid tiny houses, there are two key points to consider: connecting to a municipal water supply and a sewer system.
Connecting to a Municipal Water Supply

For those tiny houses in areas with access to municipal services, connecting to the town or city’s water supply is a straightforward option. This connection ensures a steady flow of potable water, which can be crucial for drinking, cooking, and sanitation.
The process involves setting up a water intake point on the tiny house, usually equipped with a hose or a similar connector. This intake is then linked to the house’s internal plumbing system. While the connection offers the advantage of consistent water quality and pressure, tiny house owners need to install pressure regulators and sometimes water filters. These devices protect the home’s plumbing fixtures from potential damage due to high pressure and ensure the water’s purity.
Additionally, consider incorporating water filtration systems and conservation techniques to optimize your plumbing system for maximum efficiency and tiny home sustainability.
Furthermore, considering the occasional transient nature of tiny houses, especially those on wheels, the connection setup is often designed to be easily attachable and detachable.
Connecting to a Sewer System

Similarly, on-grid tiny houses can connect directly to the municipal sewer system when it comes to waste management. Connecting to a septic system is a standard option, as it allows for the proper disposal of sewage.
This direct connection offers a hassle-free solution for disposing of both greywater and blackwater. Much like the water supply, the sewer connection involves setting up an outlet point from the house, which can be connected to the city’s sewage lines.
Some tiny houses incorporate holding tanks, which store wastewater until it can be released into the sewer system. These tanks can benefit mobile tiny houses, which might not always be near a sewer connection. This direct connection to the sewage system becomes even more essential for homes that utilize water-flushing toilets.
However, it’s vital to ensure that the connection is leak-proof and that there are mechanisms like backflow preventers to stop sewage from flowing back into the house.
Alternatively, you can explore portable toilet options that require regular emptying. To ensure clean water usage, installing water filtration systems is crucial. It’s essential to adhere to plumbing regulations for tiny homes and regularly maintain a healthy plumbing system for optimal functionality.
Off-grid
If you’re living off-grid, you’ll need to consider several key points when it comes to your water systems.
Water Storage Tanks
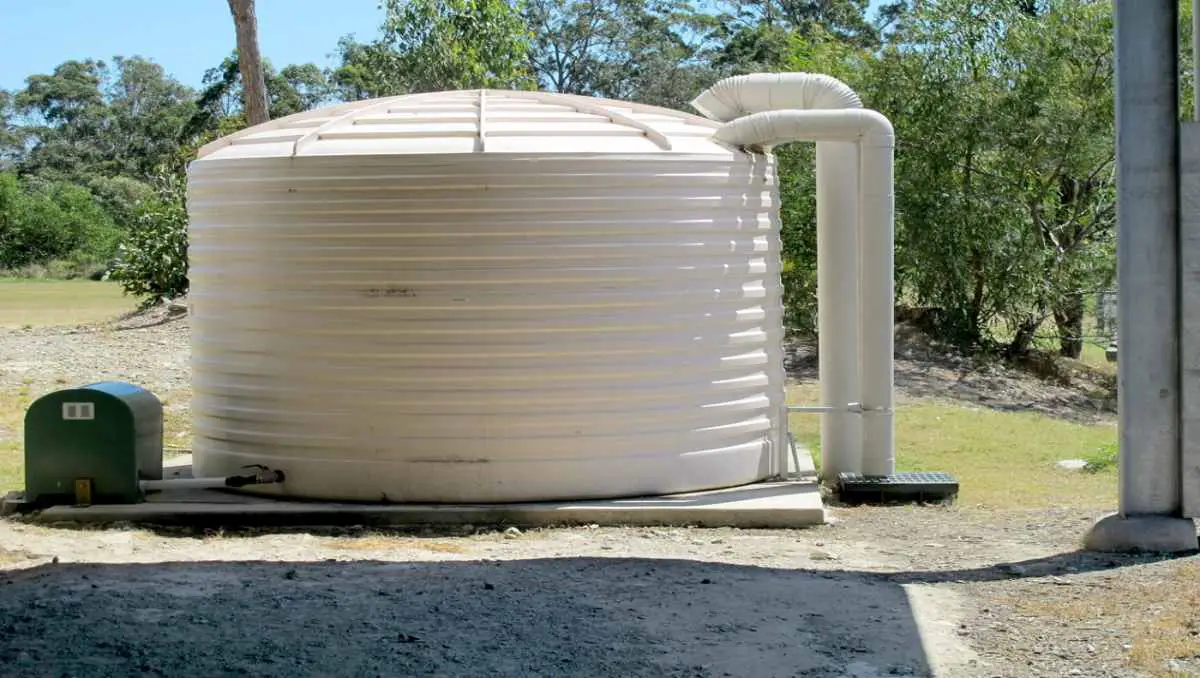

In off-grid tiny house settings, water storage tanks are indispensable. They are the primary reservoirs, often filled by harnessing rainwater from the roof.
Once collected, the water undergoes an initial filtration to remove large debris before being stored. To distribute this water throughout the house, a pump, often powered by off-grid energy sources, channels the water under pressure, ensuring a steady flow to various fixtures.
Some homes opt for gravity-fed systems, relying on elevated tanks to distribute water, though these might not offer as consistent pressure as pump systems. Before reaching taps for drinking or cooking, the water undergoes further purification, passing through sediment filters, carbon filters, and occasionally UV treatment systems to neutralize bacteria and pathogens.
For hot water, water from the storage tanks is directed through a heater, which could be powered by solar energy, gas, or electricity.
Water Pumps

The primary function of a pump in a tiny house setup is to draw water from storage tanks and deliver it under pressure to various household fixtures. This ensures that when a tap is turned on, there’s a steady flow of water, mimicking the convenience of grid-connected homes.
Depending on the specific setup, a tiny house might use different types of pumps. For instance, a diaphragm pump, known for its efficiency and compact design, is popular among many tiny homeowners.
Furthermore, when the water source is a well or a distant collection point, pumps initially transport water to the storage tanks. This ensures a consistent refill mechanism so the residents never run out of water.
Greywater Systems
Greywater systems have become integral to sustainable living, particularly in off-grid tiny houses where resource conservation is paramount. “Greywater” refers to the relatively clean wastewater from baths, sinks, washing machines, and other kitchen appliances, excluding the more contaminated water from toilets, termed “blackwater.”
In off-grid tiny house settings, greywater systems serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they reduce the amount of freshwater required by reusing water for specific tasks. For instance, rather than wasting the water used for washing hands or showering, it can be repurposed for flushing toilets or irrigating plants. This kind of recycling becomes crucial in off-grid environments where every drop of water is precious.
However, implementing a greywater system requires careful planning. The water must be filtered and sometimes treated to remove any impurities or potential pathogens, mainly if used for irrigation. Some systems use natural methods like constructed wetlands, where plants naturally filter and cleanse the water. Others involve mechanical filtration and UV treatment.
Blackwater Systems
Blackwater systems in off-grid tiny house plumbing deal with the most challenging wastewater type: the water from toilets, which contains fecal matter, urine, and toilet paper. Given blackwater’s potential health risks and environmental concerns, it is paramount to manage it properly in an off-grid setting.
In traditional plumbing, blackwater, combined with greywater, often goes to centralized sewage treatment facilities. However, alternative solutions are required in off-grid settings, especially tiny houses where connection to these centralized systems might not be feasible.
Composting toilets is one of the most popular solutions for managing blackwater in off-grid tiny houses. These units function without a regular water flush, converting human waste into compost over time.
For those tiny homes that use a water flush system, the blackwater can be stored in holding tanks, much like those in RVs. These tanks then need periodic emptying, taking the waste to appropriate disposal or treatment sites.
Drains and Waste Management Solutions
There are a few key points to consider when it comes to waste management solutions in tiny houses.
Composting Toilets
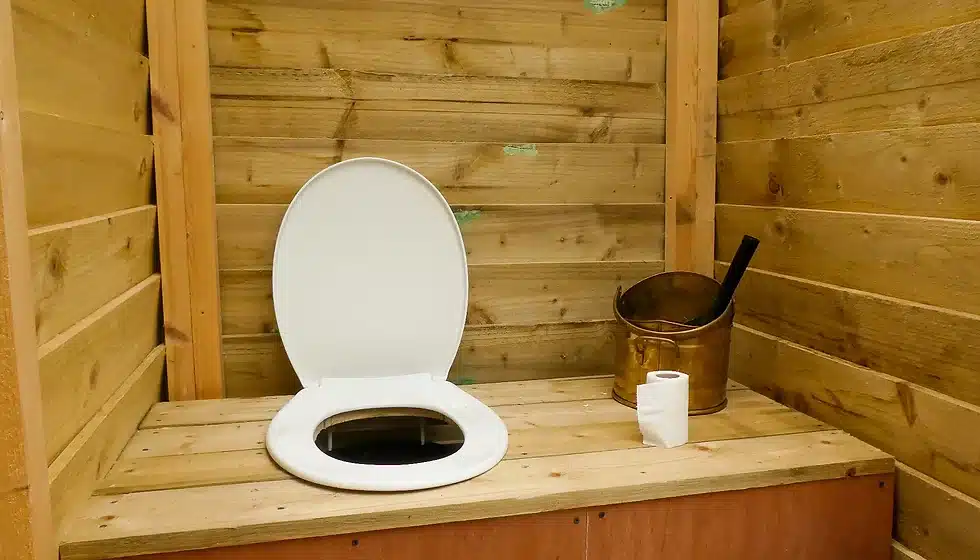

Composting or waterless toilets are an eco-friendly waste disposal solution gaining popularity among tiny house owners. These alternative toilet systems separate liquid and solid waste, allowing solids to decompose naturally through microbial activity. They use little to no water, which is especially beneficial in small living spaces where water conservation is crucial.
Composting toilets require periodic maintenance, such as adding sawdust or peat moss to aid in the decomposition process and regular emptying of the composted material. Not only do these toilets provide sustainable sanitation options for tiny houses, but they also contribute to reducing environmental impact by minimizing water usage and eliminating the need for conventional sewage systems.
Blackwater and Greywater Separation
Many tiny house owners opt for composting toilets to treat blackwater effectively, as we’ve discussed earlier. After proper treatment, greywater can be recycled for various purposes like irrigation or flushing toilets.
However, it’s crucial to note that plumbing regulations vary by location. Therefore, it’s important to consult local authorities and adhere to their guidelines when designing your tiny house plumbing system. Regular maintenance is vital to ensuring the proper functioning of your tiny home’s blackwater treatment and greywater recycling systems.
Dry Toilets vs. Flush Toilets
Opt for a dry toilet over a flush toilet to reduce water consumption and contribute to a more sustainable tiny home lifestyle. There are various dry toilet options available that can meet your needs in a tiny house. These toilets use little to no water, eliminating the need for plumbing connections. They’re environmentally friendly and comply with plumbing regulations.
Regarding water conservation, dry toilets are the way to go in tiny houses. Not only do they save precious resources, but they also simplify plumbing requirements for these small dwellings. By opting for a dry toilet, you can enjoy an eco-friendly lifestyle while meeting your sanitary needs efficiently and sustainably.
Heating and Cooling Water in Tiny Homes
In tiny home heating systems, various methods exist to achieve optimal comfort while maintaining energy efficiency and adhering to plumbing regulations.
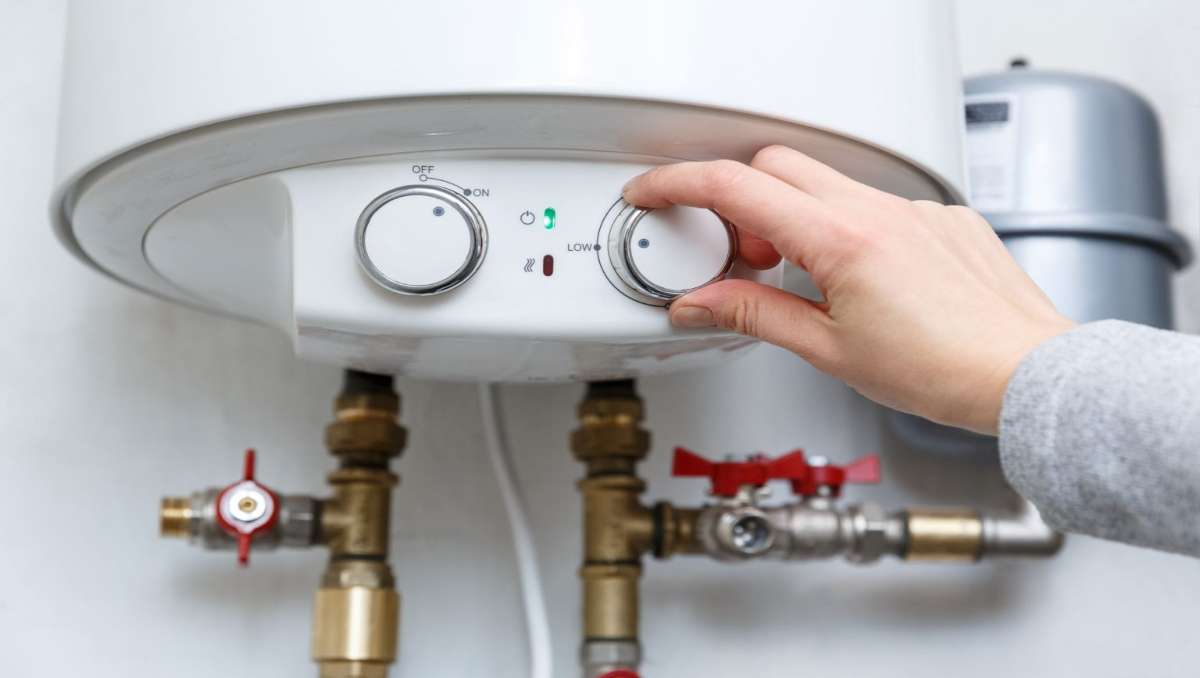

When it comes to heating water, tiny homeowners have several options. One popular method is utilizing an on-demand propane or electric water heater. These compact units instantly provide hot water without the need for bulky storage tanks, ensuring space efficiency and energy conservation.
As for cooling water in tiny homes, mini air conditioners are crucial. These compact cooling units efficiently remove heat from indoor air through evaporation or refrigeration processes. They ensure a pleasant temperature inside your humble abode while minimizing energy consumption.
To maintain sustainable practices within the limited space of a tiny home, it’s important to consider water conservation techniques such as low-flow faucets and showers, as well as dual-flush toilets that allow for different levels of flushing power depending on need.
Challenges and Solutions in Tiny House Plumbing
Regarding plumbing in your tiny home, you may encounter challenges that require creative solutions. One of the main challenges is the limited space available for plumbing systems. In a tiny house, every inch counts, so finding innovative ways to maximize efficiency is crucial.
Water Pressure: One common challenge in tiny house plumbing is water pressure. Due to smaller pipes and limited water supply, maintaining adequate pressure can be difficult. However, solutions are available, such as installing pressure regulators or utilizing gravity-fed systems to ensure consistent water flow.
Wastewater Management: Another challenge is wastewater management. Tiny homes often need more space for traditional septic systems or sewer connections. Composting toilets and greywater recycling systems are popular solutions for sustainable waste disposal in tiny houses.
Freezing: Additionally, freezing temperatures challenge plumbing in colder climates. To prevent frozen pipes, insulation, and heat tape can be used along exposed areas of the plumbing system.
Challenges in tiny house plumbing can be overcome with creative solutions tailored to the unique needs of small living spaces. By prioritizing efficient design and utilizing innovative techniques, you can enjoy a fully functional plumbing system while embracing the simplicity of tiny living.
You might be interested to learn about how long does it take to sell a tiny home.
Beyond the Pipes: Reflecting on Tiny House Plumbing Solutions
So there you have it, the ins and outs of plumbing in tiny houses. Caring for your water needs is crucial in such a small living space, from efficient systems to innovative solutions.
But remember, even with all the challenges and limitations, don’t let that deter you from pursuing the tiny house lifestyle. You can create a functional and comfortable home with proper planning and understanding of your plumbing options.







