Exploring what green building features are can be a game-changer for you, especially if you’re looking to make a positive environmental impact.
Green building features encompass a range of sustainable practices and technologies aimed at reducing the environmental impact of buildings. They include energy-efficient designs, the use of renewable energy sources, water conservation methods, and materials that are eco-friendly and promote good indoor air quality.
Curious to delve deeper into the world of green building? Our comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricacies of sustainable construction – from harnessing solar energy to innovative water conservation techniques. Keep reading to uncover the full potential of green building features and how they can transform your space into an eco-friendly haven.
What is a Green Building?
Green buildings are not just structures; they are a revolutionary approach to construction and living. They blend sustainability with innovation to create spaces that are as kind to the environment as they are to their inhabitants.
Let’s explore what makes a building ‘green’ and why it’s essential in today’s world.
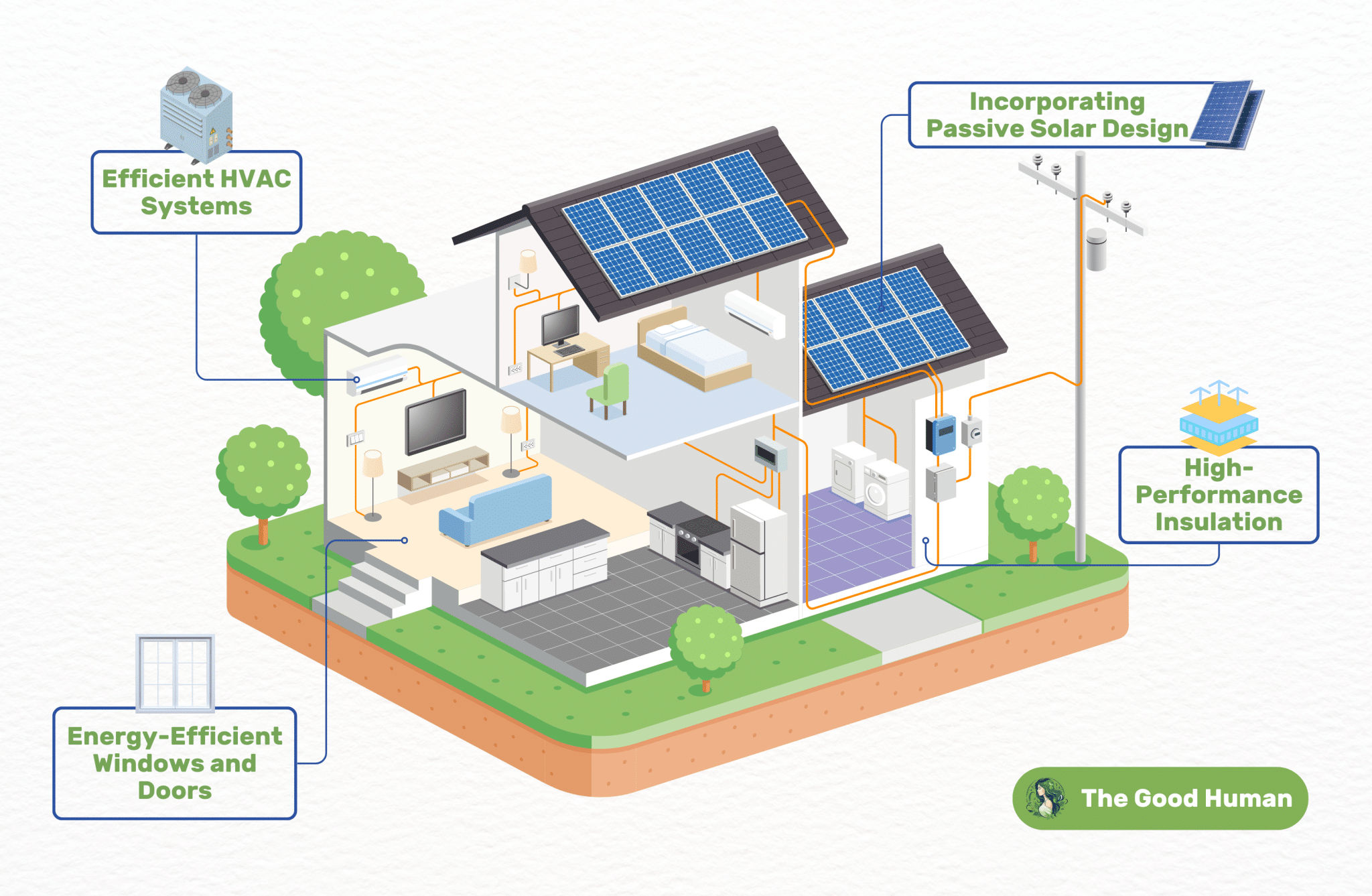
Energy-Efficient Design
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of green building design. It’s about more than just saving power; it’s about creating buildings that work in harmony with their environment. This section will explore how energy-efficient design is pivotal in reducing a building’s environmental impact.
Incorporating Passive Solar Design
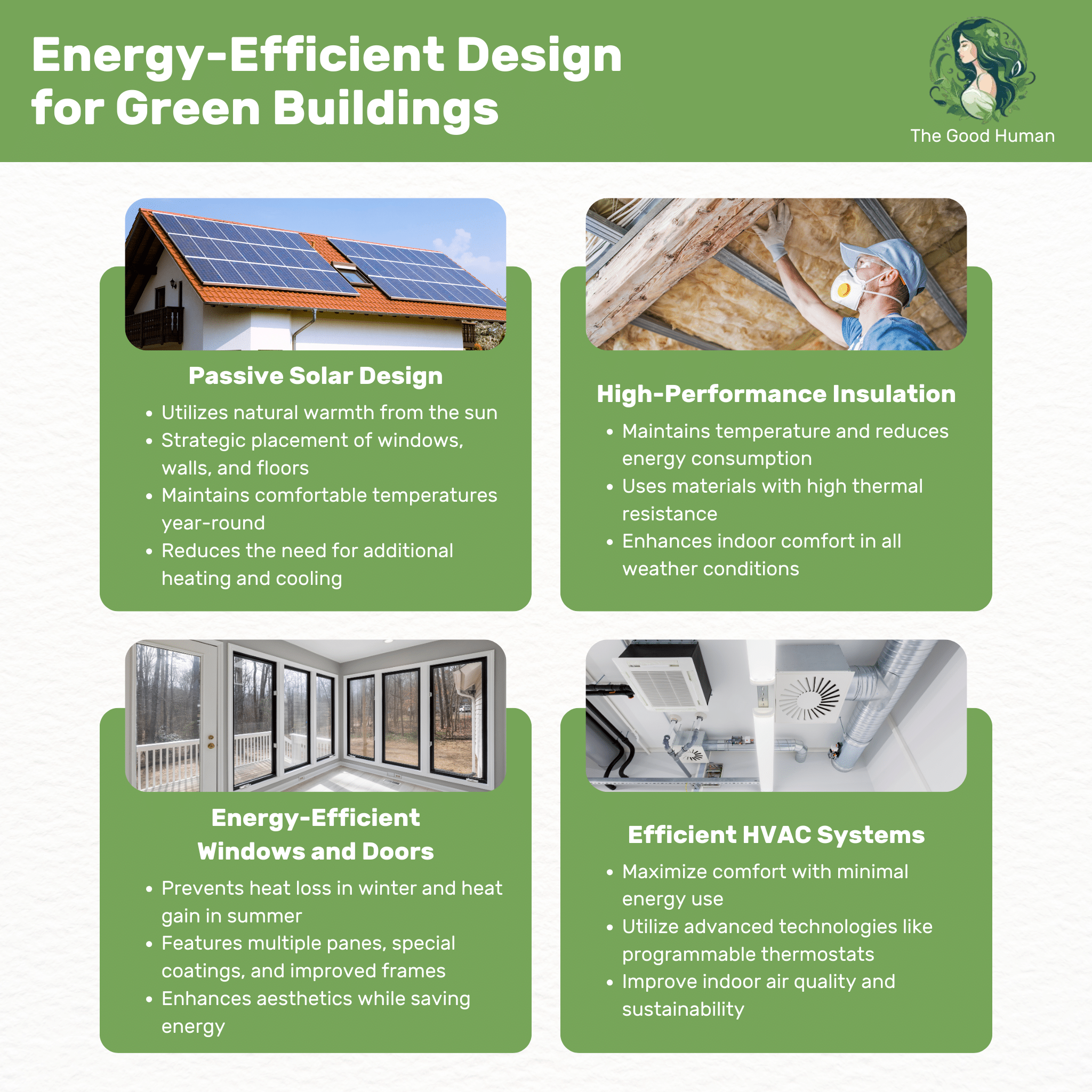
Passive solar design is a key feature of energy-efficient buildings. By utilizing the sun’s natural warmth, buildings can reduce their reliance on artificial heating. This design philosophy involves strategic placement of windows, walls, and floors to collect, store, and distribute solar energy.
The beauty of passive solar design lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. Through thoughtful orientation and design, buildings can maintain comfortable temperatures year-round, significantly reducing the need for additional heating and cooling.
High-Performance Insulation
High-performance insulation is essential in energy-efficient buildings. It plays a crucial role in maintaining temperature, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Quality insulation helps in creating a comfortable indoor environment regardless of the external weather conditions.
This type of insulation involves using materials that have a high thermal resistance. It’s not just about the thickness of the insulation but also about how effectively it prevents heat transfer. This leads to energy savings and contributes to a building’s overall energy efficiency.
Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
Energy-efficient windows and doors are vital components in green buildings. They are designed to prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, thereby reducing the energy needed for heating and cooling. These features often include multiple panes, special coatings, and improved frames.
The design of these windows and doors goes beyond functionality. They also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the building, while contributing significantly to energy savings and comfort.
Efficient HVAC Systems
Efficient HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems are the heart of a green building’s climate control. These systems are designed to provide maximum comfort with minimal energy use. They often include advanced technologies like programmable thermostats and energy-efficient motors.
Sustainable materials are the essence of green construction. They embody the concept of environmental stewardship and resource conservation. In this section, we explore how these materials make a building truly green.

Using Recycled and Reclaimed Materials
Utilizing recycled and reclaimed materials is a key practice in green building. These materials reduce the demand for new resources and minimize waste. They can include anything from reclaimed wood to recycled metal and glass.
Incorporating these materials into construction not only has environmental benefits but also adds unique character and history to the building. It’s a way of honoring the past while building for the future.

FSC-Certified Wood
FSC-certified wood is a hallmark of sustainable building. This certification ensures that the wood comes from responsibly managed forests that provide environmental, social, and economic benefits. By choosing FSC-certified wood for your construction, you’re not only ensuring the durability and quality of the materials but also supporting sustainable forestry practices.
The use of FSC-certified wood is a commitment to the environment. It reflects a dedication to preserving natural habitats, protecting water quality, and supporting the rights and welfare of workers and indigenous communities. This choice makes a profound statement about your values and your approach to responsible construction.
Low VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) Paints
Low VOC paints play a significant role in green building by improving indoor air quality. These paints emit fewer harmful chemicals than traditional paints, making them safer for both the environment and building occupants. This choice is especially important in spaces where air quality is a concern, such as homes, schools, and healthcare facilities.
The benefits of using low VOC paints extend beyond health considerations. These paints also contribute to a more pleasant and odor-free environment during and after painting. By selecting low VOC options, you’re choosing a healthier and more sustainable way to bring color and life to your spaces.
Eco-Friendly Flooring Options
Eco-friendly flooring is another aspect of sustainable materials in green building. Options like bamboo, cork, and reclaimed wood are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible. These materials come from sustainable sources and have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional flooring options.
Choosing eco-friendly flooring means considering factors like renewability, manufacturing processes, and the lifecycle of the product. This approach ensures that your flooring choices are in harmony with your commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Water Conservation
Water conservation is a critical aspect of green building. In this section, we’ll explore how innovative design and technology can significantly reduce water usage in buildings, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Low-Flow Plumbing Fixtures
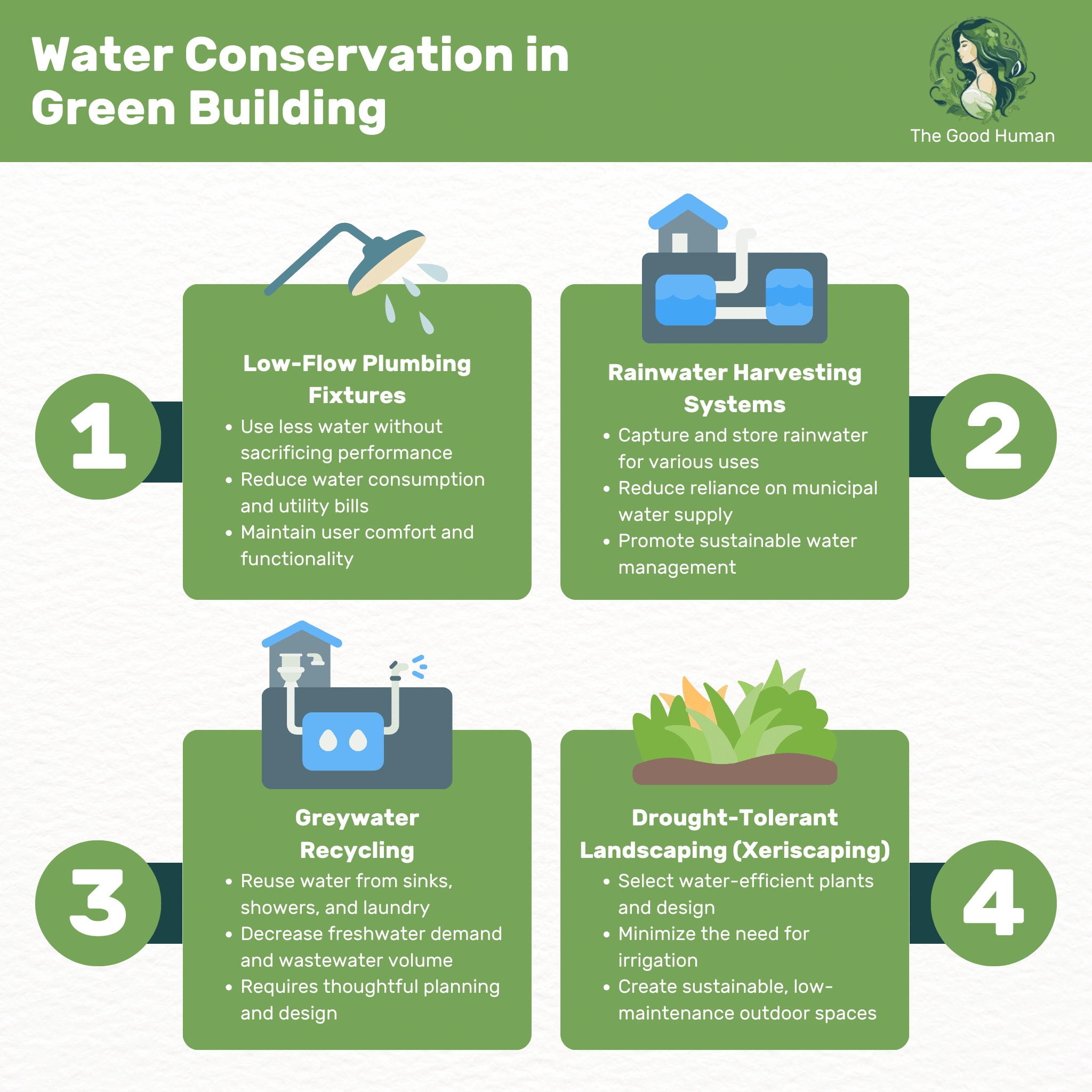
Low-flow plumbing fixtures are essential for water conservation in green buildings. These fixtures, including toilets, showerheads, and faucets, are designed to use less water without compromising performance. By installing these fixtures, you can significantly reduce water consumption and lower your utility bills.
The effectiveness of low-flow fixtures is evident not only in their water-saving capabilities but also in their ability to maintain user comfort and functionality. This makes them a practical and eco-friendly choice for any green building project.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting systems capture and store rainwater for later use, such as irrigation or even indoor non-potable uses. These systems reduce the demand on municipal water supply and help in managing stormwater runoff. By implementing rainwater harvesting, you’re taking a proactive step towards sustainable water management.
The beauty of rainwater harvesting lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. It can be as straightforward as barrels for garden watering or as complex as integrated systems for larger buildings. This practice not only conserves water but also connects you more closely with the natural water cycle.
Greywater Recycling
Greywater recycling involves reusing water from sinks, showers, and laundry for purposes like irrigation and toilet flushing. This system significantly reduces the demand for freshwater and lowers the volume of wastewater entering the sewage system. Greywater recycling is an innovative way to make the most of every drop of water used in your building.
Implementing a greywater system requires thoughtful planning and design. It’s about creating a closed-loop system that maximizes water efficiency while ensuring safety and hygiene. This approach epitomizes the essence of sustainable living.
Drought-Tolerant Landscaping
Drought-tolerant landscaping, also known as xeriscaping, is a water-efficient approach to landscaping. It involves selecting plants that require minimal water and creating a landscape design that reduces water usage. This practice not only conserves water but also creates a sustainable, low-maintenance outdoor space.
Xeriscaping is more than just choosing the right plants; it’s about understanding the local climate and soil conditions to create a harmonious, water-efficient garden. This approach can significantly reduce the need for irrigation, contributing to overall water conservation efforts.
Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality is a crucial component of green buildings, impacting the health and well-being of occupants. Let’s explore how green buildings prioritize clean air and a healthy indoor environment.
Ventilation Systems for Fresh Air
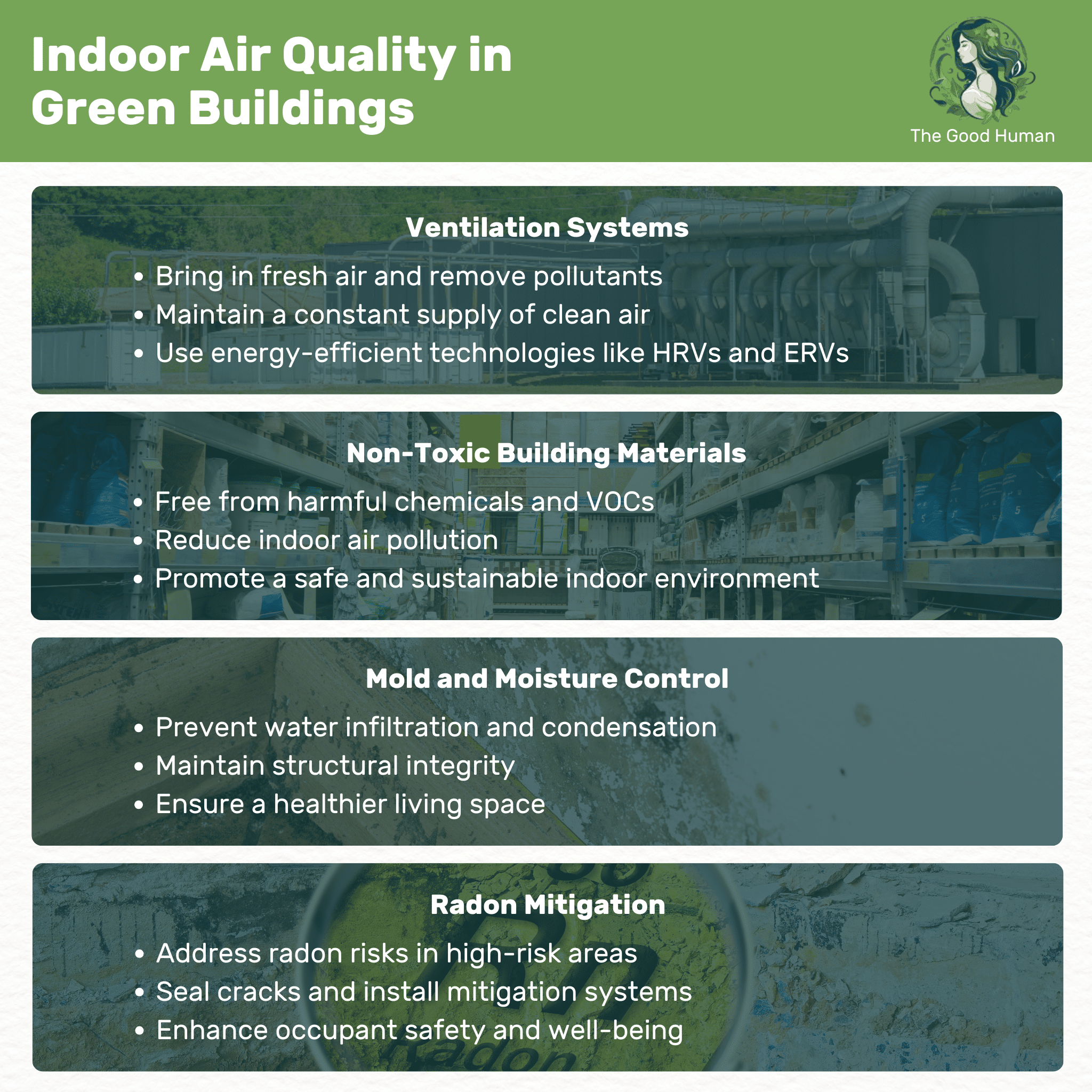
Proper ventilation is key to maintaining good indoor air quality in green buildings. Ventilation systems are designed to bring in fresh air and remove stale, polluted air, ensuring a constant supply of clean air. This is crucial for the health and comfort of building occupants.
Modern ventilation systems are not only effective but also energy-efficient. They utilize advanced technologies like heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), which help maintain indoor air quality while minimizing energy loss. By prioritizing ventilation, green buildings provide a healthier living and working environment.
Non-Toxic Building Materials
Non-toxic building materials are essential for maintaining indoor air quality. These materials, free from harmful chemicals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reduce indoor air pollution. By choosing non-toxic materials, you’re ensuring that your building is not only sustainable but also safe for its occupants.
The selection of non-toxic materials goes beyond paint and adhesives. It includes everything from flooring to insulation and furniture. By being mindful of these choices, you create a healthier indoor environment, free from pollutants that can affect the well-being of those who use the space.
Proper Mold and Moisture Control
Controlling mold and moisture is critical in green buildings to ensure a healthy indoor environment. Effective moisture management involves designing and constructing buildings in a way that prevents water infiltration and condensation. This proactive approach helps prevent mold growth and maintains the structural integrity of the building.
Strategies for mold and moisture control include proper ventilation, use of moisture-resistant materials, and diligent maintenance practices. By keeping moisture and mold in check, you not only protect the building’s structure but also ensure a healthier living space for its occupants.
Radon Mitigation
Radon mitigation is an important consideration in green building design, especially in areas prone to high radon levels. Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, can pose serious health risks if it accumulates indoors. Green buildings incorporate radon mitigation strategies to ensure the safety and health of occupants.
Effective radon mitigation includes sealing cracks and openings in the building’s foundation and installing radon mitigation systems where necessary. By addressing radon risks, green buildings enhance the overall well-being and safety of their inhabitants.
Renewable Energy Sources
Embracing renewable energy sources is a key factor in advancing the green building movement. These energy sources not only reduce dependence on fossil fuels but also significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Let’s explore the various renewable energy options that are transforming the way we power our buildings.
Solar Panel Installation
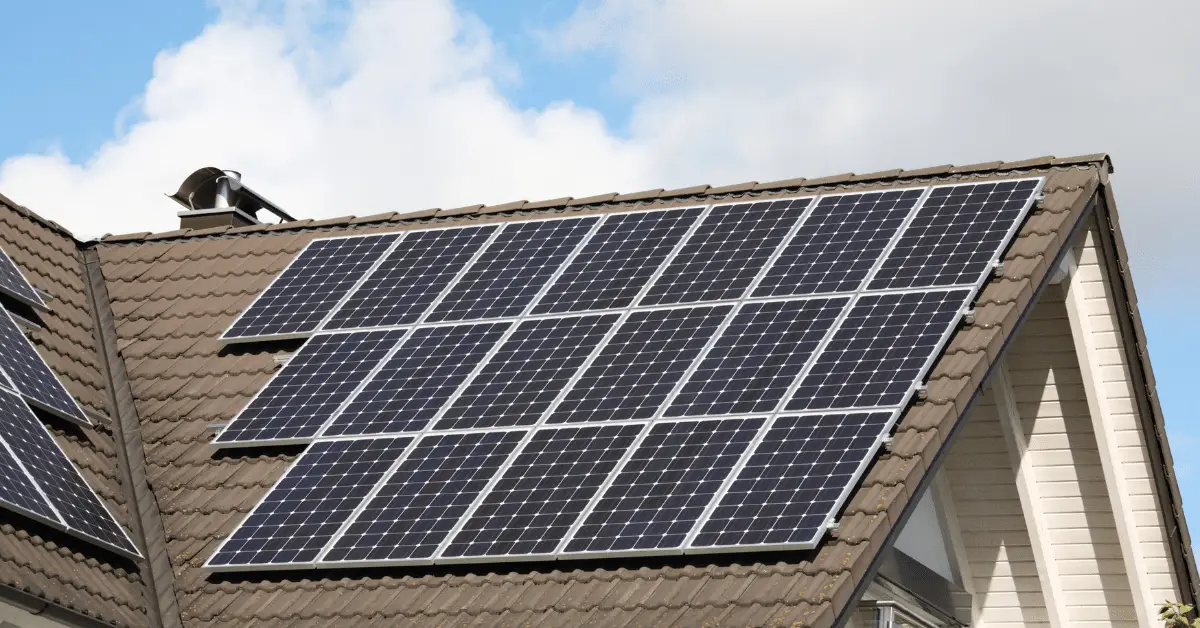

Solar panel installation is a popular choice for green buildings, harnessing the sun’s power to generate electricity. These panels can be installed on roofs or in open spaces and are effective in reducing electricity bills. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar panels offer a clean and renewable energy source.
The efficiency of solar panels has improved dramatically, making them more accessible and affordable. They are a key component in achieving energy independence and play a crucial role in reducing a building’s carbon footprint.
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are another viable renewable energy source for green buildings. These turbines convert wind energy into electricity, providing a sustainable and clean power solution. They can be installed on the building itself or in nearby open spaces.
Wind energy is particularly beneficial in areas with consistent wind patterns. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term benefits include reduced energy costs and a lower environmental impact.
Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Geothermal heating and cooling systems use the Earth’s constant underground temperature to regulate a building’s climate. This system is highly efficient and reduces reliance on traditional heating and cooling methods. Geothermal systems are known for their durability and can significantly lower utility bills.
Though the installation of geothermal systems requires an initial investment, the long-term energy savings and minimal maintenance costs make it a cost-effective choice for green buildings.
Energy-Efficient Lighting
Energy-efficient lighting is crucial in reducing a building’s energy consumption. LED lights, for instance, use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and have a longer lifespan. This not only reduces energy costs but also the need for frequent replacements.
Incorporating daylighting, where natural light is maximized, further reduces the need for artificial lighting. This approach contributes to a building’s overall energy efficiency and creates a more pleasant indoor environment.
Green Roof and Walls
Green roofs and walls represent a blend of aesthetics and functionality in green buildings. They not only improve the visual appeal of a building but also offer numerous environmental benefits. Let’s delve into the world of green roofs and walls and their role in sustainable construction.
Benefits of Green Roofs
Green roofs offer a multitude of benefits that extend beyond their visual appeal, enhancing both the environmental and functional aspects of buildings. Here’s a list of these benefits:
- Thermal Insulation: Green roofs provide natural insulation, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. This layer of vegetation acts as a barrier against extreme temperatures, maintaining a more consistent indoor climate.
- Reduced Heat Absorption: By covering the roof with vegetation, green roofs help lower heat absorption. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where the ‘heat island’ effect is prominent, as it helps in cooling down buildings and their surroundings.
- Rainwater Absorption: These roofs play a significant role in stormwater management. They absorb rainwater, thereby reducing runoff and the strain on sewage systems. This absorption also helps in preventing flooding and erosion.
- Biodiversity Support: Green roofs provide habitats for various species, particularly in urban environments where green spaces are limited. They can support a range of flora and fauna, contributing to increased biodiversity.
- Improved Air Quality: The vegetation on green roofs helps in filtering pollutants and airborne particulates. This natural filtration contributes to cleaner air around the building, benefiting both the environment and the health of the residents.
- Extended Roof Lifespan: By protecting the roofing materials from direct sun exposure and extreme weather conditions, green roofs can extend the lifespan of the roof. This protection reduces wear and tear, leading to potential cost savings in roof maintenance and replacement.
Each of these benefits contributes to the overall sustainability and efficiency of green roofs, making them a valuable addition to modern buildings, especially in urban settings.
Different Green Roof Systems: Which One’s For You?
Green roof systems are diverse, each tailored to meet specific requirements of climate, building structure, and aesthetic goals. Below are the types of green roof systems, highlighting their distinct characteristics:

Extensive Green Roofs
- These roofs are lightweight, making them suitable for large areas and buildings with lower load-bearing capacities.
- They are low-maintenance and typically feature a shallow layer of soil, supporting mosses, succulents, and other hardy vegetation.
- Extensive green roofs are ideal for creating green spaces in urban settings without the need for significant structural modifications.
Intensive Green Roofs
- These are more elaborate, allowing for a wider variety of plants, including shrubs and small trees.
- They require a deeper soil layer and more maintenance, including irrigation and regular upkeep.
- Intensive green roofs are akin to traditional gardens, offering recreational spaces and greater aesthetic diversity.
Semi-Intensive Green Roofs
- These systems combine elements of both extensive and intensive green roofs.
- They support more plant diversity than extensive roofs but require less maintenance than intensive roofs.
- Semi-intensive roofs are a versatile option, suitable for a variety of buildings and offering a balance between ecological benefits and maintenance requirements.
Tray Green Roofs
- Also known as modular green roofs, these consist of pre-planted trays or modules that can be easily installed and replaced.
- They offer flexibility in design and are convenient for buildings where access is limited.
- Tray systems are ideal for retrofitting existing buildings with green roofs.
Biodiverse Green Roofs
- Designed to mimic natural landscapes, these roofs focus on creating habitats for local wildlife.
- They often use a variety of substrates and native plant species to encourage biodiversity.
- Biodiverse roofs are particularly beneficial in urban areas where natural habitats are scarce.
Each green roof system offers its unique benefits and challenges. The choice of system depends on the specific needs of the building, the desired ecological benefits, and the level of maintenance the building owner is prepared to undertake. These green roof systems contribute significantly to urban ecology, providing much-needed green spaces in densely built environments.
Living Walls and Their Advantages
Living walls, or vertical gardens, bring a dynamic blend of aesthetics and functionality to green buildings. Here are the key advantages they offer:
- Aesthetic Enhancement
Living walls add visual interest and beauty to any space, whether it’s an exterior façade or an interior wall. They transform plain surfaces into vibrant, living art pieces, greatly enhancing the architectural appeal.
- Thermal Insulation
These walls act as natural insulators, helping to regulate the temperature within the building. They can keep interiors cooler in summer and warmer in winter, contributing to energy efficiency.
- Air Purification
Living walls improve air quality by filtering and absorbing pollutants, and producing oxygen. This is particularly beneficial in urban environments where air quality can be a concern.
- Psychological Benefits
They create a connection with nature, which can be soothing and stress-reducing for occupants. This connection to nature can enhance mental well-being, particularly in urban settings that lack green spaces.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality
By incorporating plants that remove pollutants and produce oxygen, living walls contribute to cleaner indoor air. This can lead to healthier environments for occupants, especially in densely populated or polluted areas.
- Sound Insulation
The structure of living walls can absorb sound, reducing noise pollution. This feature is advantageous in busy urban areas or in buildings where noise reduction is desired.
Living walls represent a convergence of nature and architecture, offering not just environmental benefits but also contributing to the health and well-being of building occupants. Their versatility in design and functionality makes them an increasingly popular choice in green building practices.
Smart Home Technology

The integration of smart home technology is reshaping green buildings. This technology not only enhances the efficiency and functionality of buildings but also offers greater control and monitoring of energy usage. Let’s explore how smart technology is becoming an integral part of sustainable living.
Building Automation Systems
Building Automation Systems (BAS) are at the heart of smart green buildings. These systems integrate various building functions, including heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and lighting, into a single, automated platform. This integration allows for more efficient management and reduces energy consumption.
BAS can adapt to changing conditions and occupant behaviors, optimizing the building’s performance. They are essential for maintaining a balance between comfort and energy efficiency.
Energy Monitoring and Management
Energy monitoring and management are critical components of green buildings. Advanced systems provide real-time data on energy consumption, identifying areas for improvement. This helps in making informed decisions about energy use and implementing strategies to reduce consumption.
These systems also allow for the tracking of energy usage patterns, facilitating a more proactive approach to energy management. By understanding and adjusting these patterns, buildings can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
Home Energy Management Apps
Home energy management apps are revolutionizing the way we interact with our living spaces. These apps provide users with detailed insights into their energy consumption and offer recommendations for improvement. They make managing a home’s energy usage convenient and user-friendly.
Through these apps, homeowners can monitor and control various aspects of their home’s energy use, from lighting to heating, often remotely. This level of control and awareness promotes energy-saving behaviors, aligning with the principles of green living.
Certification Programs
Certification programs play a pivotal role in the green building industry, setting benchmarks for sustainability and recognizing buildings that meet these standards. Let’s explore some of the key certification programs that are guiding the future of green building.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design)
LEED, or Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, is one of the most recognized green building certification programs worldwide. It provides a framework for healthy, highly efficient, and cost-saving green buildings. LEED certification is a symbol of sustainability achievement and leadership.
Buildings are rated based on various sustainability criteria, including energy use, air quality, and material selection. Achieving LEED certification demonstrates a commitment to environmental stewardship and social responsibility.
Passive House Certification
Passive House certification focuses on ultra-low energy buildings that require little energy for heating and cooling. This standard emphasizes super insulation, airtight construction, and energy recovery ventilation. Buildings that achieve Passive House certification are known for their exceptional energy efficiency and comfort.
This certification represents a rigorous standard for energy efficiency in a building, reducing its ecological footprint. It is a testament to sustainable design, construction, and operational practices.
ENERGY STAR Certification
ENERGY STAR certification is awarded to buildings and consumer products that meet strict energy performance standards set by the EPA. For buildings, this means using less energy, emitting fewer greenhouse gases, and saving money. ENERGY STAR-certified buildings are recognized for their energy efficiency and environmental benefits.
Achieving ENERGY STAR certification signifies that a building performs in the top 25% of similar facilities nationwide for energy efficiency. It’s a mark of excellence in energy performance.
Green Building Councils and Organizations
Green Building Councils and other organizations play a crucial role in promoting sustainable construction practices. These bodies develop standards, offer certifications, and provide resources and support for green building projects. They are instrumental in driving innovation and sustainability in the building industry.
These organizations also create platforms for collaboration and knowledge sharing, fostering a global community committed to sustainable building practices. Their work helps to elevate the importance of green building in the broader context of environmental conservation and sustainability.
Cost Considerations
Discussing cost considerations is essential when it comes to green building. While there’s an upfront investment, the long-term benefits and savings are substantial. Let’s break down the financial aspects of green building, from initial investments to long-term savings.
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
The initial investment in green building features can be higher than traditional construction. However, these costs are often offset by the long-term savings in energy, water, and maintenance. Green buildings typically have lower operating costs due to their efficient use of resources.
Investing in sustainable features like insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy sources leads to significant savings over time. This makes green buildings not only environmentally responsible but also economically smart.
Government Incentives and Rebates
To encourage sustainable building, many governments offer incentives and rebates. These can include tax credits, lower interest loans, and grants for using green technologies and materials. Such incentives significantly reduce the financial burden of adopting green building practices.
Staying informed about available incentives can make sustainable building more accessible and affordable. These incentives are a testament to the growing recognition and support for green building practices at the governmental level.
ROI of Green Building Features
The return on investment (ROI) for green building features is substantial. Improved energy efficiency leads to lower utility bills, while sustainable materials can reduce maintenance costs. Additionally, green buildings often have higher property values and market demand.
The ROI extends beyond financial gains to include environmental and social benefits. Green buildings contribute to a healthier environment and improved occupant well-being, making the investment worthwhile on multiple levels.
Final Thoughts
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on green building features, it’s clear that the journey towards sustainable construction is not just a choice but a necessity for our future. Green buildings represent a harmonious balance between environmental responsibility and modern living. They are a testament to our ability to live sustainably without compromising on comfort or functionality.
The world of green building is continuously evolving, with new technologies and practices emerging regularly. By staying informed and embracing these developments, you can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.







