Teflon, a remarkable substance known for its non-stick properties, has become a staple in many kitchens. But what happens when Teflon gets burnt? Understanding the implications of overheating this popular kitchen material is crucial for maintaining health standards in our daily cooking practices.
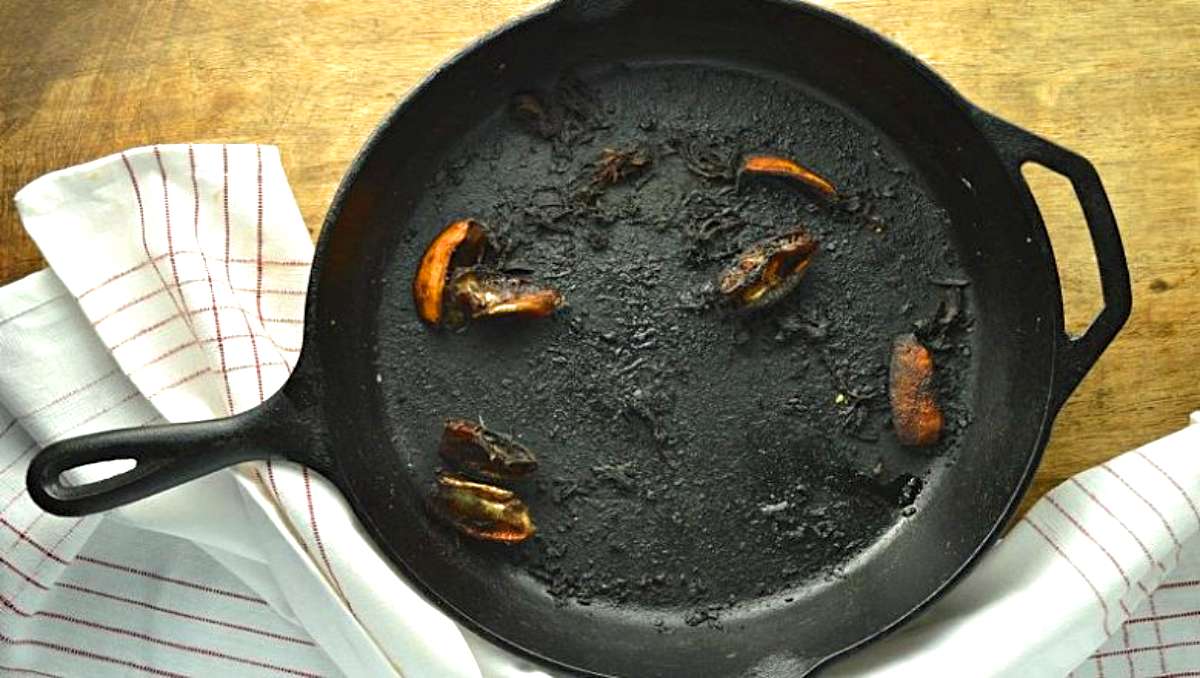
Burnt Teflon can be toxic. When heated to high temperatures, Teflon can release toxic fumes, including perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Inhaling these fumes, typically above 500°F (260°C), can lead to polymer fume fever and other health risks.
This article provides an objective and scientific exploration of the risks associated with burnt Teflon and how it can potentially impact your health and our environment.
What is Teflon Made of? How Does it Work?
Did you know that Teflon, the non-stick wonder in your kitchen, is made up of a magical combination of carbon and fluorine atoms that come together to create a slick surface like no other?
The manufacturing process of Teflon involves heating a mixture of carbon and fluorine gases at high temperatures. This causes the atoms to bond tightly, creating a unique structure that gives Teflon exceptional non-stick properties.
Teflon’s non-stick abilities are due to its low surface energy. This means that liquids and solids have difficulty adhering to their surface, making it perfect for applications such as cooking pans or industrial coatings where sticking can be an issue.
Its chemical stability is another critical feature, as it can withstand high temperatures without breaking down or releasing toxic fumes.
The bonding mechanisms between the carbon and fluorine atoms make Teflon incredibly durable. These bonds are strong and resistant to wear and tear, ensuring the non-stick coating remains intact after repeated use. Additionally, Teflon has excellent resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for use in various industries.
Properties of Teflon
Teflon possesses unique characteristics that make it a popular choice for various applications. Some key properties of Teflon include:
- Non-stick: Teflon has exceptional non-stick properties, preventing food and other substances from adhering to its surface. This quality makes it widely used in cookware.
- Low Friction: Teflon exhibits low friction, making it an ideal material for applications where reduced friction is essential, such as in bearings and slide plates.
- Chemical Resistance: Teflon is highly resistant to chemicals, acids, and solvents. This property makes it suitable for use in laboratory equipment, chemical processing, and as a lining for containers.
- Thermal Stability: Teflon can withstand high temperatures without significant degradation. Its high melting point makes it suitable for cooking at elevated temperatures.
- Electrical Insulation: Teflon is an excellent electrical insulator, making it valuable for applications in the electronics industry, including insulating wires and cables.
- Low Surface Energy: Teflon has a low surface energy, contributing to its non-stick properties and making it resistant to wetting by liquids.
While Teflon offers these advantages, it is crucial to note that it can release fumes that pose health concerns when heated to high temperatures.
The Risks of Burnt Teflon
When Teflon is heated, its chemical composition undergoes changes that can pose potential risks. Burnt Teflon may release toxic fumes, making it important to understand the effects of inhaling these substances.
Considering the evolving landscape of Teflon safety, especially with recent discussions on some Teflon ban in some countries, staying informed about these developments is crucial for a safer and healthier cooking environment.

Chemical Composition Changes When Teflon is Heated
Heating Teflon causes a transformation in its chemical composition. When Teflon is heated, it undergoes a process called thermal decomposition. This results in the breakdown of the Teflon molecule and the release of various chemicals and gases.
One of the main concerns with burnt Teflon is the potential release of toxic fumes, such as perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and fluorine gas. These substances can be harmful to human health if they are inhaled or ingested. Additionally, heating effects can lead to the formation of carbon monoxide gas, which is also toxic.
It is important to note that these chemical changes occur when Teflon is exposed to high temperatures beyond its recommended cooking range. To ensure safety, it is advisable to avoid overheating or burning Teflon-coated cookware.
Is Burnt Teflon Toxic? Understanding PTFE and PFOA
When it comes to burnt Teflon, understanding its toxicity is crucial for our well-being.
Teflon is made from a chemical called polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is generally considered safe when used correctly. However, when heated above 500 degrees Fahrenheit, PTFE can release toxic fumes that may cause flu-like symptoms in humans and death in pet birds. These fumes contain PFOA, a chemical linked to various health risks.
To ensure safety while using Teflon, avoid overheating your pans, use ventilation when cooking at high temperatures, and discard any scratched or damaged Teflon cookwares.
Health Effects Associated with Inhaling Teflon Fumes

Protecting your health is essential, and understanding the health effects of inhaling Teflon fumes is crucial. When Teflon is heated to high temperatures, it can release toxic fumes that have been linked to respiratory and pulmonary effects and other adverse health outcomes.
Inhalation of Teflon fumes can cause symptoms like coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Long-term exposure to these fumes may lead to more severe respiratory issues and even lung damage.
Taking safety precautions when using Teflon-coated cookware is essential to minimize toxic exposure. By being aware of these potential risks and taking necessary precautions, you can ensure a safer cooking environment for yourself and your loved ones.
Detecting Burnt Teflon
There are several key signs to look out for to detect burnt Teflon. Firstly, you may notice a strong and unpleasant odor when cooking with Teflon-coated cookware. This smell indicates that the Teflon has started to degrade and burn.
Additionally, if you see any visible signs of discoloration or flaking on the cookware’s surface, it could be a sign that the Teflon coating has been damaged and is potentially releasing toxic fumes when heated.
Signs of Teflon Degradation and Burning
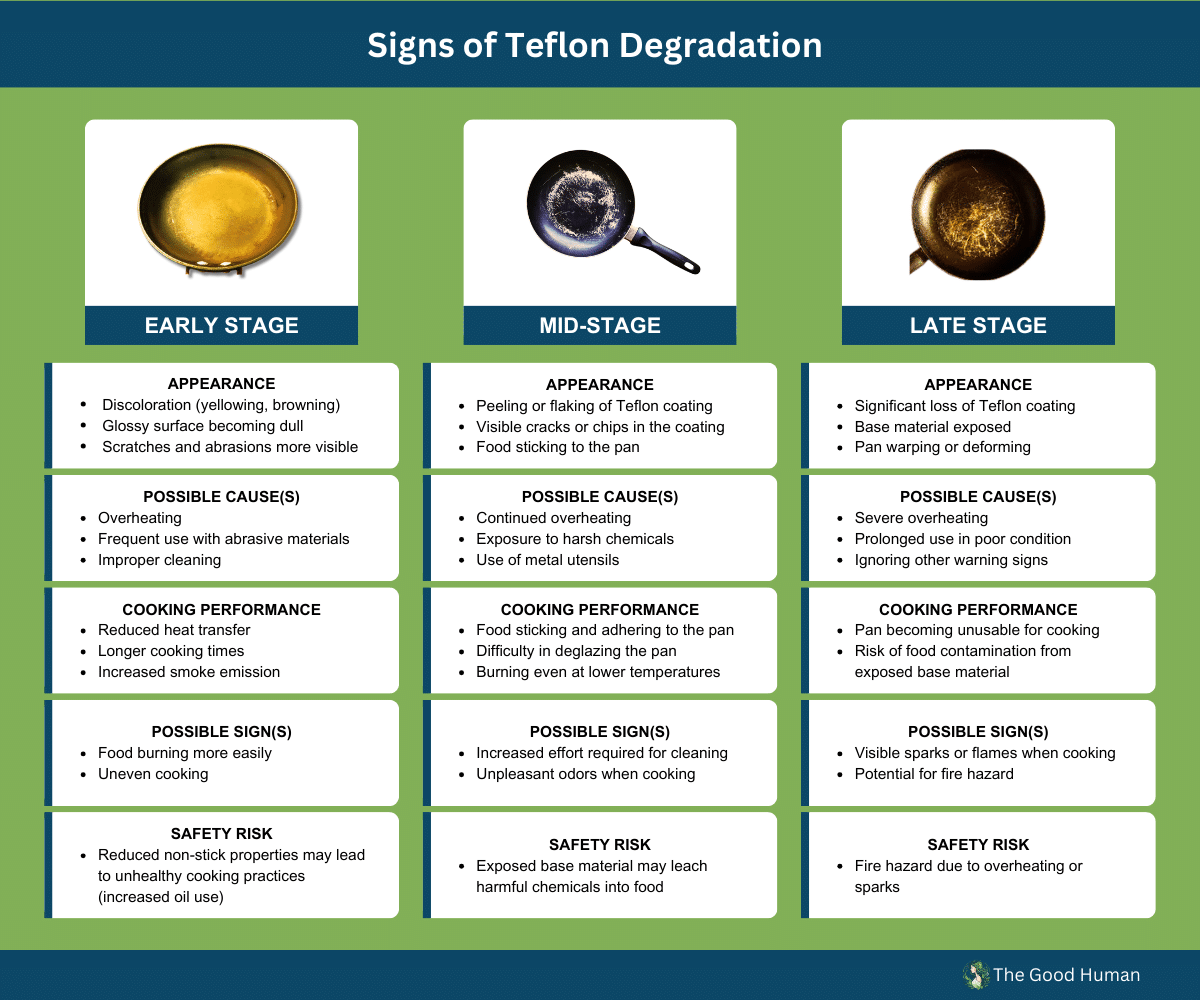
As Teflon degrades and burns, it releases a noxious odor akin to the stench of a smoldering fire. Detecting Teflon degradation is crucial to mitigate potential health risks and take appropriate safety precautions.
When Teflon undergoes thermal stress or overheating, chemical changes can lead to its degradation and burning. One of the most noticeable signs of Teflon degradation is the release of toxic fumes. It is essential to be aware of these signs and take immediate action if you detect them.
If your Teflon cookware shows any signs of burning or peeling, it is recommended to replace it immediately to ensure your safety and prevent further exposure to potentially harmful substances.
Who is Most at Risk From Burnt Teflon Exposure?
The most vulnerable groups when it comes to burnt Teflon exposure include individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The fumes from overheated Teflon can exacerbate their symptoms and potentially lead to respiratory distress.
Pregnant women are also at higher risk due to the potential harm that these fumes can cause to the developing fetus.

To ensure safety, it is important to follow proper cooking practices and adhere to safety guidelines provided by Teflon manufacturers. These guidelines often include avoiding high heat settings, using ventilation systems while cooking, and keeping an eye on food being cooked in Teflon-coated cookware.
Cooking Safety Tips with Teflon
When cooking with Teflon cookware, it is important to properly manage the temperature to avoid overheating and burnt Teflon. Overheating can release toxic fumes and damage the nonstick coating. Knowing when to replace Teflon cookware and considering alternatives if necessary for a safe and healthy cooking experience is crucial.
Proper Temperature Management for Teflon Cookware
Temperature control is crucial because excessive heat can damage the Teflon coating and release toxic fumes. Avoid using high heat settings or preheating an empty pan, as this can lead to overheating. Instead, opt for medium to low heat settings when cooking with Teflon.
Additionally, consider using cooking techniques that distribute heat evenly, such as simmering or sautéing. This helps prevent hot spots and reduces the risk of burning the Teflon surface.
When cleaning your Teflon cookware, use gentle methods like handwashing with mild soap and avoid abrasive scrubbers that may damage the coating. Regular maintenance, like avoiding metal utensils and inspecting for signs of wear, also contributes to the longevity of your Teflon cookware.
Avoiding Overheating and Burnt Teflon
Ensure the longevity and safety of your Teflon cookware by avoiding excessive heat that can lead to damage. Preventing overheating is crucial in maintaining proper temperature control and avoiding burnt surfaces.
When using Teflon cookware, keep a close eye on the heat level to prevent it from exceeding the recommended temperature range. High temperatures can cause the non-stick surface to deteriorate, releasing toxic fumes that may be harmful when inhaled. To maintain heat management, use low to medium heat settings while cooking with Teflon pans or pots.
Knowing When to Replace Teflon Cookware
Knowing when to replace Teflon cookware is very important. The average lifespan of Teflon cookware should only be around 3-5 years. Over time, Teflon coating can degrade, making it less effective at preventing food from sticking and potentially releasing harmful chemicals.
One obvious sign to look out for is visible scratches or flaking on the cookware’s surface. These areas can expose the underlying metal, leading to uneven heating and compromised non-stick properties.
Another indication that it is time to replace your Teflon cookware is when you notice a decline in its performance. If food starts sticking more frequently or you need to use more oil or butter than usual, it could be a sign that the coating has worn off.
Alternatives to Teflon Cookware
Several alternatives to Teflon cookware are available, offering different features and benefits. Here are some popular alternatives:
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to scratching and durable. It doesn’t have a non-stick coating, but proper preheating and using oils or fats can prevent sticking.
- Cast Iron: Known for excellent heat retention and even heating, cast iron cookware develops a natural non-stick surface when properly seasoned. It requires regular maintenance to keep the seasoning intact.
- Ceramic: Ceramic-coated cookware provides a non-stick surface without PTFE or PFOA. It is generally safe at high temperatures, but care should be taken to avoid chipping the ceramic coating.
- Carbon Steel: Like cast iron, carbon steel develops a non-stick surface with seasoning. It is lighter than cast iron and heats up quickly, making it suitable for various cooking styles.
- Hard-Anodized Aluminum: This aluminum cookware has been treated to make it harder and more durable. It often comes with a non-stick coating that is more resistant to scratching than traditional Teflon.
Industry Standards and Regulations for Teflon Products
To understand the safety of burnt Teflon, you should be aware of the industry standards and regulations for Teflon products. These regulations ensure that Teflon products meet specific safety requirements and are suitable for use in various applications.
Safety standards encompass a range of factors, including product compliance, quality control, and manufacturing guidelines. The industry has established strict regulations to address concerns regarding the potential release of toxic fumes from overheating or burning Teflon cookware.

The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the main regulatory body overseeing these standards. They have set limits on the amount of PFOA, a chemical used in producing Teflon, that can be present in products.
Manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure consumer safety. These guidelines outline proper manufacturing processes and materials to minimize any potential risks of Teflon usage. Regular inspections and testing are conducted to verify compliance with these standards.
It is important to note that while adherence to industry standards helps mitigate risks, proper usage and care of Teflon cookware also play a crucial role in maintaining its safety. Avoiding high heat settings and replacing damaged or worn-out cookware are all essential practices for prolonging the lifespan and ensuring safe usage of Teflon products.
Environmental Impact of Burnt Teflon
The environmental consequences of overheated or charred Teflon pans can have far-reaching implications. When Teflon is heated above 500 degrees Fahrenheit, it releases toxic fumes that can harm humans and the environment.
When burnt Teflon pans are discarded improperly, they contribute to pollution in landfills. The chemicals released from these pans can contaminate soil and water sources, posing a threat to plants, animals, and ecosystems. Handling and disposing of burnt Teflon pans responsibly is important to minimize their environmental impact.
When disposing of damaged or worn-out Teflon pans, it is best to check with local recycling centers for specific guidelines on recycling or hazardous waste disposal.
Cooking Confidence: Safety First in Teflon Handling
In conclusion, being aware of the risks associated with burnt Teflon is very important. The toxic fumes released when Teflon is overheated can harm your health. However, you can minimize these risks by following cooking safety tips and being vigilant in detecting burnt Teflon.
As consumers, being aware of proper usage guidelines, avoiding overheating, and considering alternative cookware materials are vital steps in minimizing potential health risks associated with Teflon.







