In today’s eco-conscious world, many gardeners are turning to sustainable planting techniques to nurture their gardens. These methods not only enhance the health of your garden but also contribute positively to the planet.
Sustainable planting techniques involve selecting native plants, conserving water, and encouraging biodiversity in the garden. These practices promote a healthy ecosystem, reduce environmental impact, and support the well-being of local wildlife.
Curious about how you can make your garden a beacon of sustainability? From the soil under your fingernails to the pollinators buzzing through your flowers, every aspect of your garden holds potential for positive impact. Dive into our guide on sustainable planting techniques to discover how easy and rewarding it is to grow a garden that benefits you, your community, and the environment.
What is Sustainable Planting?
Sustainable planting might sound complex, but it’s essentially about making choices in your garden that support the long-term health and prosperity of the planet. This includes using resources in a way that doesn’t deplete them and ensuring that the garden contributes positively to the environment.

By choosing plants that are well-suited to your local climate and soil, minimizing water usage, and avoiding chemical pesticides and fertilizers, you’re already on your way to a more sustainable garden.
It’s not just about reducing your environmental footprint; it’s about creating a space that flourishes naturally and requires less intervention over time.
Adopting sustainable planting practices means you’re looking at your garden as part of a larger ecosystem. This approach encourages biodiversity, supports local wildlife, and enhances soil health.
By observing and mimicking natural processes, you can create a garden that’s not only beautiful and productive but also resilient and self-sustaining. It’s a shift from the traditional view of gardening towards a more holistic and environmentally friendly approach.
How Sustainable Planting Supports Ecosystems and Garden Vitality
Sustainable planting goes beyond just choosing the right plants; it’s about creating an environment where your garden can thrive while supporting the ecosystems around it.
By emphasizing biodiversity, you encourage a variety of life forms to call your garden home, from beneficial insects to birds and small mammals. This variety not only makes your garden more resilient to pests and diseases but also contributes to the health of local ecosystems.
Moreover, sustainable gardens play a critical role in supporting pollinators, which are essential for the reproduction of many plants and the production of fruits and vegetables. By providing a haven for these creatures, you’re contributing to the health of the wider environment.
Sustainable planting practices ensure that your garden is a place of refuge for these vital members of the ecosystem, helping to counteract the effects of habitat loss and environmental degradation. In doing so, you’re ensuring that your garden is not just a place of beauty, but a vital contributor to the planet’s health.
Soil Health and Management
Healthy soil is the foundation of any garden, especially a sustainable one. It’s the bedrock that supports plant life, providing them with the nutrients, air, and water they need to thrive. By focusing on building and maintaining healthy soil, you’re ensuring that your garden can grow lush and vibrant with minimal external inputs.
Essential Steps to Achieve Optimal Soil Health
The first step towards healthy soil is understanding its current condition. This means getting your hands dirty—literally.
By conducting a soil test, you can determine its composition, pH, and nutrient levels, allowing you to tailor your gardening practices to meet its specific needs. Adding organic matter, such as compost, is a key strategy for improving soil health.
Compost not only enriches the soil with nutrients but also improves its structure, enhancing its ability to retain water and air, which are critical for plant growth.
Healthy soil is also about fostering a living ecosystem beneath your feet. This includes encouraging earthworms and beneficial microbes that break down organic matter, aerate the soil, and help make nutrients available to plants.
By avoiding the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, you protect these invaluable soil inhabitants, ensuring that your garden is built on a foundation of vibrant, life-supporting soil.
Soil Improvement Techniques That Work
Improving your garden’s soil might seem daunting, but with a few practical techniques, you can see significant improvements.
Mulching is a simple yet effective method. By covering the soil with organic material like straw, leaves, alum, or wood chips, you not only conserve moisture but also suppress weeds and gradually improve soil quality as the mulch breaks down.
Here’s an overview of what mulching is:

Another technique is crop rotation, especially if you’re growing vegetables. By planting different crops in different areas each year, you can help prevent soil depletion and reduce pest and disease problems.
This practice ensures that your soil remains healthy and fertile, supporting a more productive and sustainable garden. By integrating these techniques into your gardening routine, you’ll build a robust foundation that will sustain your garden year after year.
Water Conservation Strategies
In a world where water is becoming increasingly precious, conserving this vital resource in your garden is more important than ever. Sustainable planting includes strategies that minimize water use while ensuring your plants get the hydration they need. It’s about being smart with water, using it efficiently, and reducing wastage.
One of the simplest ways to conserve water is by collecting rainwater. Using barrels or a rainwater harvesting system, you can capture water during rainy periods to use in your garden during drier times.
This not only reduces your reliance on tap water but also makes use of a free and natural resource. Additionally, watering your plants in the early morning or late evening can minimize evaporation, ensuring that more water goes directly to your plants where it’s needed most.
Choosing plants that are native to your area or that are drought-resistant can also significantly reduce your garden’s water needs. These plants are adapted to your local climate and soil conditions, requiring less water and maintenance than non-native species.
By selecting the right plants for your garden’s environment, you can create a beautiful, resilient landscape that thrives with minimal watering.
Here’s a list of drought-resistant plants you may want to include in your garden:
- Lavender
- Sedum
- Echinacea
- Sage
- Yucca
- Agave
- Cactus
- Russian Sage
- Lamb’s Ear
- Thyme
- Portulaca
- Aloe Vera
- Bougainvillea
- Rosemary
- Succulents
Innovative Water-Saving Techniques for the Eco-Conscious Gardener
Beyond traditional methods, there are innovative techniques to further reduce your garden’s water footprint. Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the base of each plant, minimizing waste and ensuring that water goes exactly where it’s needed. Similarly, designing your garden with water conservation in mind, such as grouping plants with similar water needs together, can make a significant difference in how much water your garden consumes.
Another technique is using mulch and ground covers to reduce evaporation from the soil surface. This not only conserves water but also adds to the health of your soil, creating a more sustainable garden ecosystem.
By adopting these water-saving strategies, you’re not just conserving a crucial resource; you’re also creating a garden that’s more in tune with the natural world, ensuring it remains lush, productive, and vibrant for years to come.
Plant Selection and Biodiversity
Choosing the right plants for your garden is like picking friends who make your life richer and more colorful. It’s not just about what looks good; it’s about finding plants that fit well into your garden’s environment and contribute to a more balanced and sustainable ecosystem. When you focus on plant selection and biodiversity, you’re working towards a garden that’s not only beautiful but also resilient and beneficial to the local wildlife.

Native plants are the superheroes of the garden world. They’ve adapted to your local climate and soil, which means they’re more likely to thrive with less fuss. By choosing native plants, you’re not just making your gardening life easier; you’re also providing essential habitats for local birds, bees, and butterflies. These plants are a key part of the ecosystem, offering the food and shelter that these creatures need to survive.
Incorporating native varieties into your garden also means you’re less likely to need chemical fertilizers and pesticides. These plants have natural resistances to local pests and diseases, reducing the need for intervention.
Plus, they’re better at managing water, which can help to conserve this precious resource. Overall, native plants offer a win-win situation: they’re low maintenance for you and fantastic for the environment.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
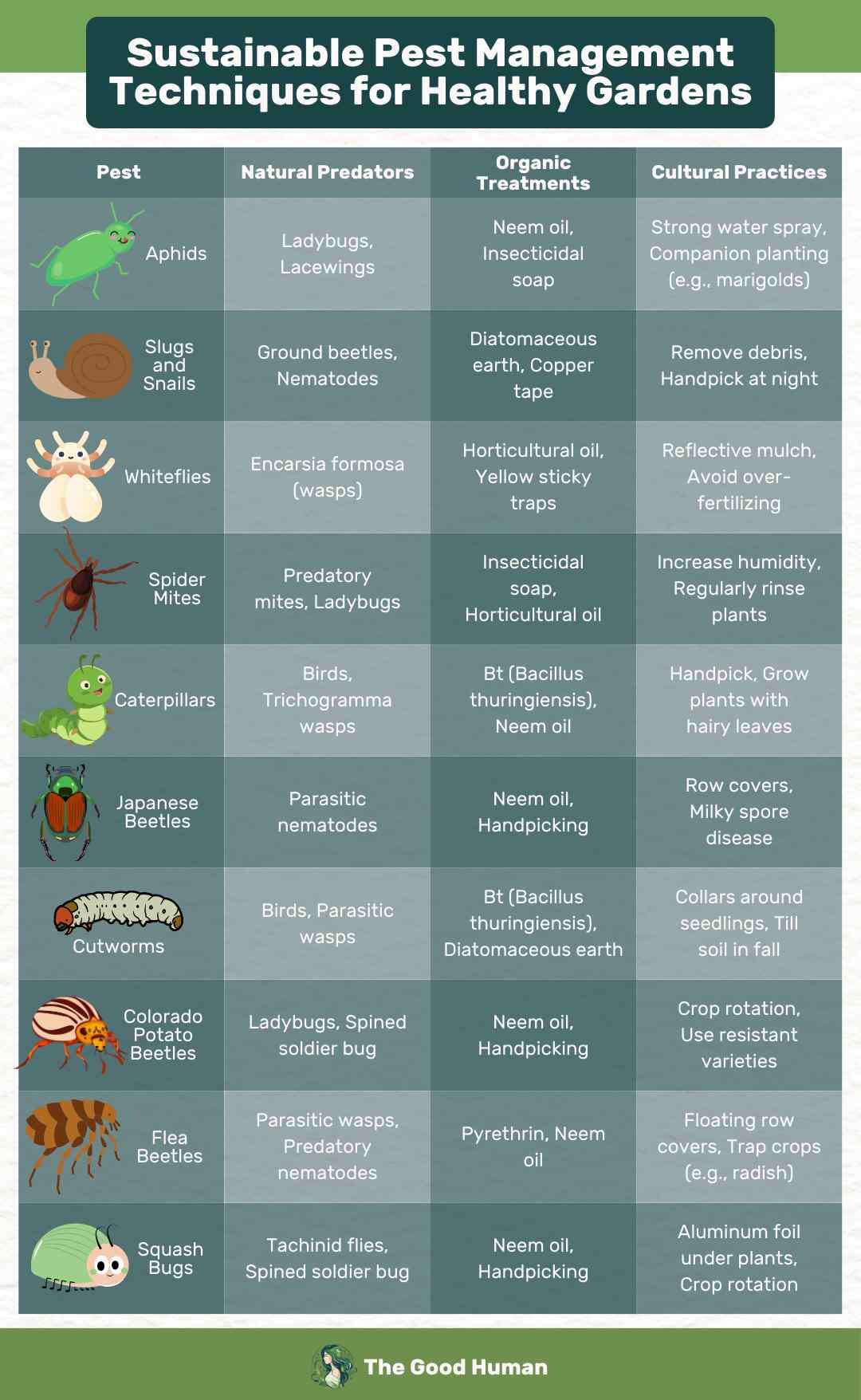
Pests are a fact of gardening life, but how you deal with them can make a big difference to your garden’s health and the environment. Integrated Pest Management, or IPM, is a smart way to manage pests that minimizes risks to people, plants, and the planet. It’s about using a variety of methods to control pests, starting with the least harmful and only moving to chemicals as a last resort.
Eco-Friendly Pest Control: Starting with Nature’s Way
The first step in eco-friendly pest control is to get to know your garden. Understand which pests are common and observe how they interact with your plants.
Often, the best way to control pests is to prevent them from becoming a problem in the first place. This can be as simple as choosing disease-resistant plant varieties or altering your watering habits to discourage pests that thrive in damp conditions.
Encouraging natural predators is another key strategy. Birds, ladybugs, and lacewings are just a few of the garden helpers that eat common pests. You can attract these beneficial creatures by planting a variety of plants and providing water sources and shelter. This way, nature does much of the pest control work for you, without the need for harmful chemicals.
Implementing IPM in your garden means being proactive. Regularly inspecting your plants for signs of pests or disease helps you catch problems early when they’re easier to manage.
If pests do appear, identify them correctly so you can choose the most effective and least harmful control method.
Sometimes, physical barriers like nets or row covers can protect your plants without the need for any chemicals. And if it comes to using pesticides, opt for targeted, less toxic options and apply them carefully, following the instructions to the letter. Remember, the goal of IPM is not to eradicate all pests but to manage them in a way that keeps your garden healthy and minimizes environmental impact.
Here’s an overview of the different types of pests and how you can best deal with them:
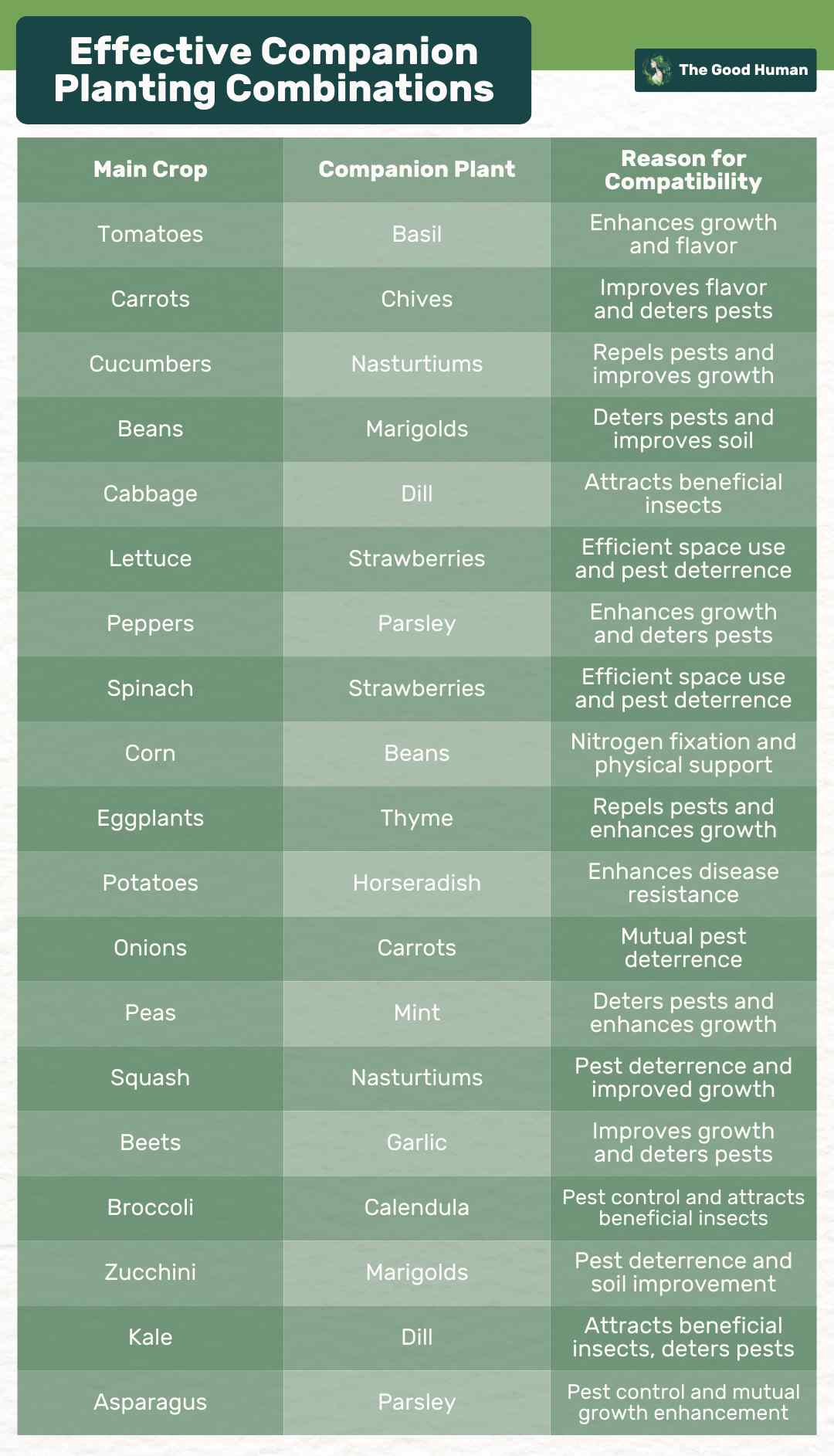
Companion Planting
Certain plants, when grown together, can help each other out. For example, marigolds release a scent that repels many garden pests, making them great companions for tomatoes and peppers.
Similarly, planting basil near your tomatoes can help to improve their flavor. It’s not just about pest control; companion planting can also improve soil health, provide shade or support, and maximize space in your garden.
Companion planting is a sustainable way to enhance your garden’s ecosystem. It encourages a diverse range of plants and insects, creating a more balanced and healthy garden environment. Plus, it’s a chemical-free way to boost your garden’s productivity and health, making it a win-win for you and the planet.
Encouraging Beneficial Insects
Attracting beneficial insects starts with diversity. Planting a variety of flowers and herbs can provide the nectar and pollen that many beneficial insects need to survive.
Flowers like marigolds, sunflowers, and lavender are not only beautiful but also work hard to attract insects like ladybugs, bees, and lacewings, which help control pests. Additionally, allowing a part of your garden to grow a little wild can create a welcoming habitat for these allies.
Another key to encouraging beneficial insects is to avoid using pesticides, which can harm not only pests but also the beneficial insects that help keep those pests in check. Instead, focus on creating a balanced ecosystem in your garden where insects can naturally keep pest populations under control. This approach not only supports a healthier garden but also promotes biodiversity.
To effectively recruit beneficial insects, consider incorporating plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season to provide a constant food source.
Companion planting can also be a powerful tool in your arsenal, as certain plant combinations can significantly increase the attraction of beneficial insects. For example, planting dill or fennel can attract predatory insects that feast on common garden pests.
Remember, water is as important to insects as it is to plants. Including features like a shallow bird bath or a dripping irrigation hose can ensure that beneficial insects stay hydrated and happy in your garden.
By taking these steps, you’re not just gardening; you’re curating an ecosystem that supports and sustains a rich variety of life.
Composting and Organic Matter
Starting a compost pile is easier than you might think. All you need is a balance of greens, like vegetable scraps and coffee grounds, and browns, such as leaves and cardboard, to create a mix that decomposes into rich compost.
Keeping the pile moist and turning it regularly speeds up the decomposition process, turning your waste into garden gold in a matter of months. This homemade compost is far superior to any fertilizer you could buy, feeding your plants and improving your soil structure.

The benefits of composting extend beyond just nutrient-rich soil. It also improves soil aeration and water retention, making your garden more drought-resistant. By introducing compost to your garden, you’re not only recycling waste but also creating a healthier, more vibrant ecosystem right in your backyard.
According to Garden Lively’s Community Garden Statistics 2023, community gardens can significantly impact local communities by increasing surrounding property values, yielding a substantial amount of fresh produce, and dramatically lowering household food security concerns.
Additionally, for every dollar invested in a community garden, approximately six dollars’ worth of produce can be generated, underscoring the economic and social value of these gardens. This emphasizes the interconnectedness of individual actions like composting and broader community benefits.
Advanced Composting Techniques for Serious Gardeners
For those looking to take their composting to the next level, exploring methods like worm composting or bokashi can be rewarding. Worm composting, or vermicomposting, uses red wiggler worms to break down scraps more quickly, producing high-quality compost and liquid fertilizer.
Bokashi composting, a method originating from Japan, ferments kitchen waste, including dairy and meat, into compost through an anaerobic process, offering a faster turnaround than traditional composting.
These advanced techniques can fit into even the smallest of spaces, making composting accessible to everyone. To know more about these methods, you can check the table below:

And if you’re unsure where to start, here’s a beginner’s guide to starting your own compost system:
Supporting Pollinators and Wildlife
Creating a garden oasis for pollinators and wildlife starts with plant selection. Choose a variety of native plants that provide nectar and pollen sources throughout the year. Including plants with different shapes, colors, and bloom times will attract a wider range of pollinators. Additionally, features like bird feeders, nesting boxes, and a source of water can make your garden even more inviting to wildlife.
Remember to avoid pesticides, as they can harm the very creatures you’re trying to attract. Instead, focus on building a balanced ecosystem where predators and prey can keep each other in check naturally. By doing so, you create a garden that’s not only a haven for wildlife but also a place where you can enjoy the beauty and diversity of nature right on your doorstep.
Sustainable Materials and Tools for the Conscious Gardener
Eco-friendly gardening starts with selecting tools and materials that are durable, made from sustainable materials, or recycled. Look for tools made from stainless steel or wood from sustainably managed forests. Choose pots made from biodegradable materials or repurpose containers you already have. By making these choices, you reduce waste and support sustainable practices in manufacturing.
Consider also the products you use in your garden. Opt for organic gardening by using organic fertilizers and pest control methods that won’t harm the earth. By choosing sustainable materials and tools, you’re not just taking care of your garden; you’re taking care of the environment that supports us all.
Making the switch to sustainable gardening tools and practices is easier than you might think. Start small by replacing one or two items with more sustainable options, and gradually incorporate more eco-friendly practices into your gardening routine. Remember, every small change contributes to a larger impact on the health of our planet.
Whether it’s using a rain barrel to collect water for your garden, choosing solar-powered garden lights, or making your own compost, there are countless ways to embrace sustainable gardening. By making these changes, you’re joining a growing community of gardeners who are committed to nurturing their gardens and the planet in harmony.
Final Thoughts
As you reflect on these sustainable planting techniques, remember that every small step you take makes a difference. Whether it’s choosing native plants, making your own compost, or providing a haven for wildlife, each action contributes to a healthier, more sustainable garden and planet.
Gardening is not just about the beauty and bounty it brings to our lives; it’s also about the legacy we leave for future generations. By adopting these practices, you’re not just growing plants; you’re cultivating a greener world.







