Have you ever wondered what does a woman’s pheromones smell like? It’s a question that taps into the invisible chemistry of attraction, drawing us closer to understanding how subtle scents play a role in human connections.
Describing the scent of female pheromones varies widely, ranging from sweet and floral to musky and earthy, influenced by individual chemistry and biological factors.
Dive deeper into the science and mystery behind the scents that drive attraction and compatibility. Discover how diet, genetics, and even the menstrual cycle can alter and enhance these elusive signals, shaping the way we perceive and are drawn to each other.
Understanding Pheromones: Nature’s Invisible Communication
Pheromones play a crucial role in the way animals and humans interact with their environment and each other, acting as chemical messengers that convey important social and reproductive signals.
By understanding how pheromones work and the different types that exist, we can gain insight into the complex world of non-verbal communication that influences behavior and attraction.
How Do Pheromones Work?
Pheromones are chemical substances produced by an organism that, when released into the environment, trigger a natural response in another member of the same species. These invisible chemical signals are detected through the olfactory system and can influence a wide range of behaviors, including aggression, territoriality, and mating practices.
The process is largely subconscious, allowing for an instinctual reaction that is not governed by conscious thought but by a deep-rooted biological mechanism. This ensures seamless communication within species, guiding social interactions and reproductive activities without the need for verbal communication or visual cues.
The complexity of pheromones in humans adds an intriguing layer to their study. While humans do produce substances that can be classified as pheromones, the extent to which these influence our social and sexual behavior is still under research. The Vomeronasal Organ (VNO), thought to be pivotal in detecting pheromones in many animals, is present in humans, yet its functionality remains a topic of debate among scientists.
Despite this, evidence suggests that human behavior and attraction can be influenced by chemical signals, albeit in a more nuanced and less deterministic manner than in the animal kingdom. Adding to this complexity, George Preti of the Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philadelphia notes, “That doesn’t mean a human sex pheromone doesn’t exist,” he adds, “It just means we haven’t found one yet.” This statement underscores the ongoing exploration and scientific curiosity surrounding the role of pheromones in human attraction and social interaction.
Types of Pheromones and Their Functions
Before diving into the different types of pheromones, it’s important to note that these chemical messengers are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each type serves a distinct purpose, facilitating various forms of communication within a species.
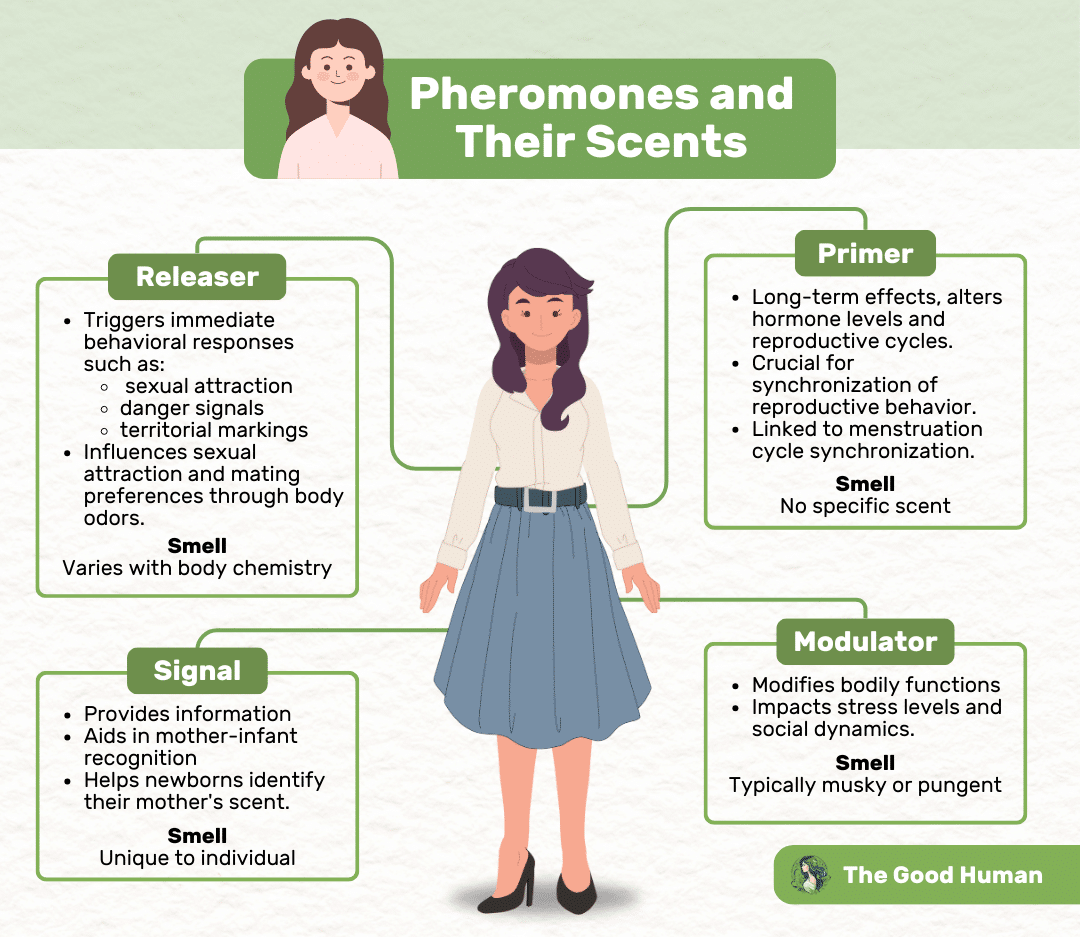
Here’s a closer look at the major pheromones and their functions:
Releaser Pheromones
These pheromones trigger an immediate behavioral response in the recipient. Commonly observed in the animal kingdom, releaser pheromones can prompt sexual attraction, signal danger, or mark territory. In humans, their role is seen in sexual attraction, where certain body odors can increase attractiveness to potential mates, subtly influencing mating choices and preferences.
Primer Pheromones
Unlike releaser pheromones, primer pheromones have a long-term effect on the behavior and physiology of the recipient. They can alter hormone levels, affecting reproductive cycles and readiness for mating. In many species, these pheromones ensure synchronization of reproductive behavior, making them crucial for the survival of species. In humans, the evidence for primer pheromones is suggestive but less concrete, with some studies indicating their role in menstruation cycle synchronization among women living in close proximity.
Signal Pheromones
Signal pheromones provide information. They can mark trails leading to food, signal a threat, or identify an individual’s territory. Ants, for example, use signal pheromones to lead others to a food source. In humans, these types of pheromones may play a role in mother-infant recognition, helping newborns identify their mother’s scent shortly after birth.
Modulator Pheromones
Found in sweat, these pheromones can modify or synchronize bodily functions. In animals, modulator pheromones can adjust stress levels or impact social dynamics within a group. Human studies suggest that exposure to certain pheromones in sweat can affect mood and stress levels, indicating a subtle but impactful way our bodies communicate stress and comfort levels to each other.
The Scent of Female Pheromones

Pheromones, often dubbed nature’s silent communicators, play a significant role in various aspects of human interaction, including attraction and social bonding. While the existence and impact of pheromones are widely acknowledged, understanding the nuances of a woman’s pheromones and their scent is a topic that continues to pique scientific curiosity.
The Science Behind Pheromone Production
Pheromones are chemical compounds secreted by various glands throughout the body, including the apocrine glands located in areas such as the armpits and genital region. These glands release pheromones into the environment, where they can influence the behavior and physiology of individuals around them.
Several factors can influence the production and release of pheromones in women. Hormonal fluctuations, genetic predispositions, and environmental stimuli all play a role in determining the quantity and composition of pheromones emitted by an individual.
While the general purpose of pheromones remains consistent—communication and signaling—there is considerable variability in the specific scent of pheromones among women. This variation can be attributed to genetic differences, personal hygiene habits, dietary choices, and even cultural factors. Consequently, each woman’s unique blend of pheromones contributes to her distinct scent profile.
The notion of altering or enhancing pheromone scent raises intriguing questions about the potential for manipulating human attraction and social dynamics. While there are products marketed as pheromone enhancers, their efficacy and scientific validity remain subjects of debate. Some argue that personal hygiene and lifestyle choices can indirectly influence pheromone production and perception, but the extent to which these factors can be intentionally modified to alter pheromone scent is uncertain.
Describing the Smell of Female Pheromones
The scent of female pheromones is a complex and subtle signal that plays a significant role in attraction and communication. Understanding how they are described and the factors influencing their scent offers insight into their biological and social functions.
Common Descriptors
The subtle yet impactful nature of female pheromones lies in their ability to convey crucial information about fertility and compatibility through scent. These aromas, which blend seamlessly with an individual’s natural body odor, can vary widely from person to person, influenced by biological and environmental factors.
The descriptors “sweet and floral” or “musky and earthy” only scratch the surface of the complex scent profiles that can be emitted. This variability ensures that each individual’s pheromone signature is unique, playing a key role in the intricate dance of human attraction and social interaction.
Moreover, the perception of these scents is not merely a matter of olfactory detection but involves a complex interplay with our brain’s interpretation of these chemical signals. The fact that these scents operate on a subconscious level means that they can influence our social and romantic interactions in profound ways, often without us ever becoming consciously aware of them.
The ability of pheromones to blend with and enhance natural body odors contributes to a multi-layered communication system, where chemical signals can dictate attraction and compatibility beyond what is visible to the eye.
Pheromones and Body Odor
The interplay between pheromones and body odor is a delicate balance, where each can influence the perception of the other. Pheromones, as specialized chemical signals, are intricately linked to an individual’s body odor, which is itself a complex mixture of various compounds influenced by genetics, diet, and hygiene. This relationship means that the natural scent of an individual can carry subtle hints about their reproductive status and genetic makeup, serving as cues in the complex realm of human attraction.
Adjustments in hygiene practices can modulate the presence of pheromones in body odor, potentially enhancing or diminishing their natural effect. While strong body odors may be masked or reduced through hygiene, the underlying pheromone signals remain, continuing to influence social and sexual interactions on a subconscious level.
Influences on Pheromone Scent
Several factors can influence the scent of pheromones, highlighting the dynamic nature of this chemical communication.

Diet
The impact of diet on pheromone scent is significant, with certain foods enhancing or altering the natural body scent. Foods rich in spices, garlic, and other strong flavors can seep into body secretions, modifying the pheromone profile. Conversely, a diet high in fruits and vegetables may result in a sweeter, more appealing scent, suggesting that what we consume can directly affect how we are perceived by others.
Genetics
Genetics play a foundational role in determining the composition and scent of an individual’s pheromones. Genetic diversity is often signaled through pheromones, attracting potential mates by indicating a beneficial mix for offspring. This genetic interplay ensures that pheromone signals are as unique as fingerprints, contributing to the complexity of human attraction and social interaction.
Hygiene
Hygiene practices can influence the intensity and purity of pheromone signals. Regular washing can reduce the strength of body odors, including pheromones, potentially masking natural signals intended for mate attraction. However, a balance must be struck, as overly aggressive hygiene practices can eliminate these important chemical cues, disrupting natural social signaling.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors, including stress, exercise, and sleep patterns, can also affect pheromone production and scent. Stress can alter body odors, making them more pungent or unpleasant, while regular exercise is thought to enhance the natural pheromone profile. Adequate sleep and overall health contribute to the optimal production and release of pheromones, emphasizing the importance of a balanced lifestyle in maintaining and enhancing personal scent profiles.
Pheromones and Attraction
Pheromones serve as a fundamental element in the complex arena of attraction, facilitating an unspoken communication between individuals. They influence not only the physical attraction but also the deeper, subconscious preferences that guide mate selection.
Pheromones and Mate Selection
Within the context of mate selection, pheromones play a crucial role in signaling compatibility and health to potential partners. This chemical communication aids in the subconscious assessment of genetic suitability, paving the way for deeper connections.
Role in Sexual Attraction

The concept of sexual attraction mediated by pheromones delves into the biological essence of human interaction, highlighting a non-verbal communication that predates modern societal constructs. These chemical signals, deeply embedded in our evolutionary journey, serve as a catalyst for attraction, subtly guiding us towards partners with complementary genetic profiles.
This phenomenon not only bolsters genetic diversity but also enhances the survival and health of future progeny. The nuanced dance of attraction, influenced by pheromones, underscores an instinctual drive towards optimal reproductive partnerships, weaving a complex web of desire and compatibility that transcends conscious thought.
Subconscious Signals
Pheromones orchestrate a myriad of subconscious cues that influence human behavior and preferences in a profound way. These chemical messengers, silent yet potent, trigger a cascade of emotional and physiological reactions, setting the stage for attraction and compatibility.
This under-the-radar communication system allows individuals to navigate the social landscape, making split-second judgments about potential mates without the need for direct interaction. The intricate role of pheromones in shaping our social and sexual behaviors highlights their critical influence on the dynamics of human relationships.
The Connection Between Pheromones and Ovulation
The interplay between pheromones and ovulation presents a fascinating glimpse into the subtleties of human reproduction. As a woman’s body goes through the menstrual cycle, the variation in pheromone production signals her fertility status to potential mates, influencing perceptions of attractiveness.
This biological signaling mechanism, deeply rooted in our evolutionary past, plays a pivotal role in mate selection, subtly guiding sexual behavior and preferences. The dynamic nature of this chemical communication illustrates the profound ways in which our bodies convey reproductive readiness and attractiveness.
Pheromones in Same-Sex Attraction
In the realm of same-sex attraction, pheromones emerge as a universal language of compatibility and desire, transcending gender boundaries. The ability of individuals to be subconsciously drawn to the pheromones of those with complementary genetic makeups highlights the adaptive nature of this chemical communication.
This phenomenon underscores the breadth of pheromones’ influence, demonstrating their role in fostering a sense of attraction and compatibility across the spectrum of human sexuality. The study of pheromones in same-sex attraction enriches our understanding of the biological underpinnings of attraction, revealing a layer of complexity in how we connect and form bonds.
The Influence of Hormones and Menstrual Cycle

The complex interplay between hormones and the menstrual cycle plays a crucial role in the production and perception of pheromones. These biological processes significantly influence not only how pheromones are emitted but also how they are received by others.
The Effect of Hormones on Pheromone Production and Scent
Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle can alter the composition and intensity of pheromones produced by the body. During ovulation, for example, estrogen levels peak, potentially enhancing the production of pheromones that signal fertility and attractiveness.
This hormonal surge can lead to a change in a woman’s natural scent, making her more appealing to potential mates. The subtle changes in pheromone composition can communicate reproductive readiness, playing a key role in sexual attraction and mate selection.
Moreover, these hormonal shifts can affect the body’s overall scent, not just pheromones. The varying levels of hormones can influence sweat production and the body’s natural odors, contributing to a distinct scent profile at different points in the menstrual cycle. This means that a woman’s scent can provide unconscious cues about her fertility status, adding layers to the complexity of human attraction and interaction.
The Menstrual Cycle and Its Role in Pheromone Attractiveness
The menstrual cycle’s impact on pheromone attractiveness is a fascinating aspect of human biology. Research suggests that men may subconsciously perceive changes in women’s pheromone signals throughout their cycle, with a preference for the scents produced during the ovulatory phase. This period, characterized by higher fertility, may see women emitting stronger or more appealing pheromone signals, attracting the opposite sex more effectively. Such biological cues play a significant role in the natural selection process, guiding mating behaviors and preferences.
This attraction is not merely about the emission of more potent pheromones but also about the synchronization of biological and behavioral cues that signal fertility. The changes in a woman’s appearance, behavior, and scent during ovulation can all contribute to increased attractiveness, showcasing the nuanced ways in which the menstrual cycle influences human sexual behavior and perceptions of attractiveness.
How the Menstrual Cycle Alters Pheromone Perception
The menstrual cycle’s influence extends to the perception of pheromones, where shifts in hormonal levels can affect how pheromones are detected and interpreted. For instance, some studies suggest that women may become more attuned to certain scents, including pheromones, during their fertile phase, potentially aiding in mate selection. This heightened olfactory sensitivity could play a role in identifying genetically compatible partners, emphasizing the importance of scent in human reproductive strategies.
Conversely, the perception of pheromones can also fluctuate in potential mates, who may become more sensitive to these signals during a woman’s fertile window. This reciprocal enhancement of pheromone production and perception underlines the intricate biological dialogue facilitated by the menstrual cycle, contributing to the complex dance of human attraction and mate selection.
Final Thoughts
The intricate relationship between pheromones, hormones, and the menstrual cycle highlights the profound impact of biological processes on human attraction and social interaction. These natural signals, often operating below the threshold of conscious awareness, play a vital role in guiding mating behaviors and preferences, underscoring the deep biological underpinnings of human relationships. As research continues to unravel these complex interactions, we gain further insight into the subtle ways in which our bodies communicate in the realm of attraction and compatibility.







